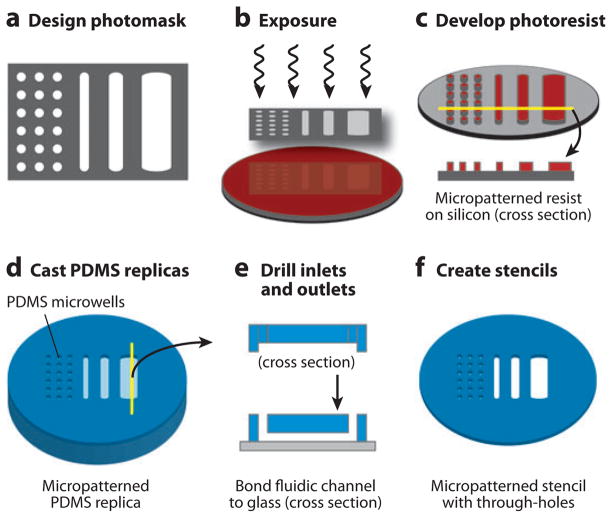
Figure 5.
Microfabrication and soft lithography. (a) Photomasks are drawn using a computer-aided design tool and are printed by a high-resolution printer on mylar transparency films. (b) Photoresist-coated silicon wafers are exposed through the photomask and (c) developed to translate the photomask design to the silicon surface. (d) The silicon then serves as a master mold for casting transparent polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) polymer replicas, which can be (e) drilled to create inlets and outlets and bonded to a glass substrate to create closed microfluidic devices or (f) used to create stencils with micropatterned through-holes.