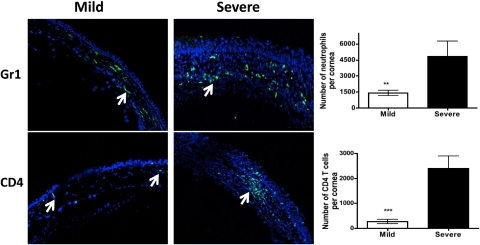
Figure 6.
The corneas with severe HSK demonstrate a significantly higher number of neutrophils and CD4 T cells when compared with those with mild disease. Six-micrometer frozen sections were obtained from the eyes that developed mild or severe HSK lesions as determined on Day 15 postinfection. Sections were stained for neutrophils and CD4 T cells (green) followed by acquisition on a confocal microscope (C1 Nikon; magnification ×20). Arrows denote Gr1+ neutrophils and CD4 T cells in the corneas with mild or severe HSK lesions. The corneas with mild or severe HSK lesions were collagenase-digested on Day 15 postinfection followed by staining for CD4 T cells and neutrophils. The samples were acquired by flow cytometry and absolute numbers were calculated from the proportion of cell types. Three corneas with mild HSK lesions were pooled together to obtain one sample whereas four corneas with severe HSK were pooled to obtain one sample. A total of three to four samples were obtained from two experiments. Graphs indicate the absolute number of cells within the cornea as determined by flow cytometry. Data represents the mean ± SEM of two independent experiments. P values were calculated using Student's t-test (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).