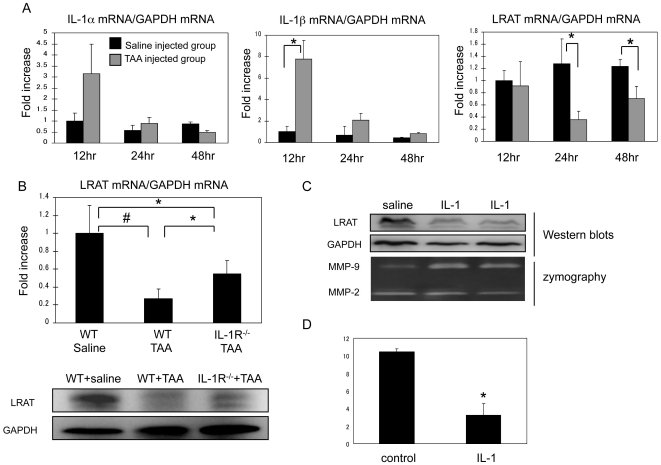
Figure 7. Interleukin-1 mediates down-regulation of LRAT in acute liver injury by mouse model.
(A) Acute liver injury in WT mice was induced by challenge with TAA (0.2 mg/g body weight) via i.p. injection. Saline was used for control. Time course of mRNA levels for LRAT, IL-1α, and IL-1β in the liver was measured by qRT-PCR. Results (mean ± SD) are expressed as folds of increase related to the saline injected group (n = 5). (B) To determine the contribution of IL-1 toward injury-induced down-regulation of LRAT, IL-1R−/− and WT mice were subjected to TAA injection. After 24 hours, mRNA level of LRAT was measured by qRT-PCR. Results (mean ± SD) are expressed as folds of increase relative to normal saline-injected WT mice. *P<0.05, #P<0.01. LRAT protein expression was assessed by Western blot. GAPDH: loading control. (C) WT mice were intravenously injected with recombinant IL-1α protein (20 ng) or saline for 24 hours. LRAT and MMP-9 levels in the liver tissues were examined by Western blot and zymography analysis respectively. (D) Hepatic retinyl palmitate levels after IL-1 injection for 24 hours were measured by LC/MS/MS using liver tissues from mice receiving intravenous injection of IL-1α (20 ng) or saline. *P<0.01 (n = 4/group).