Abstract
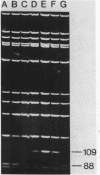
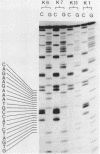
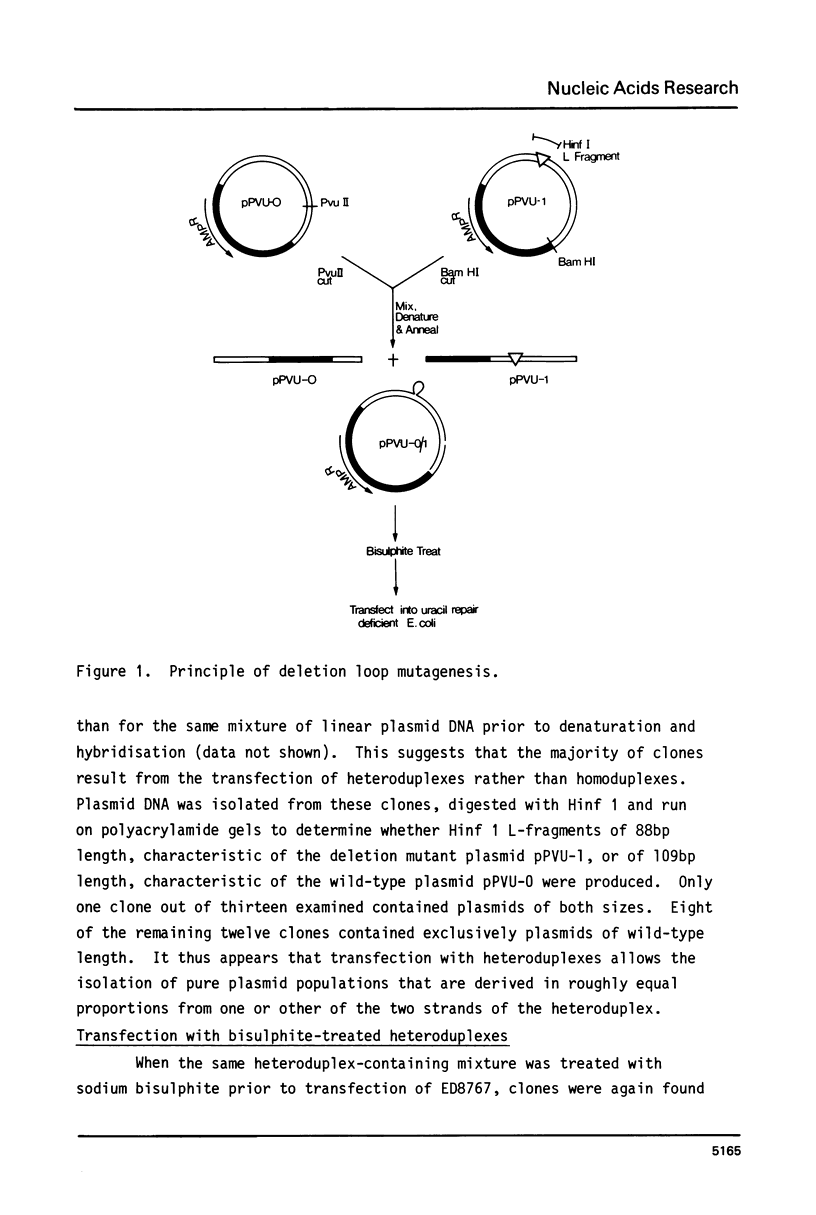
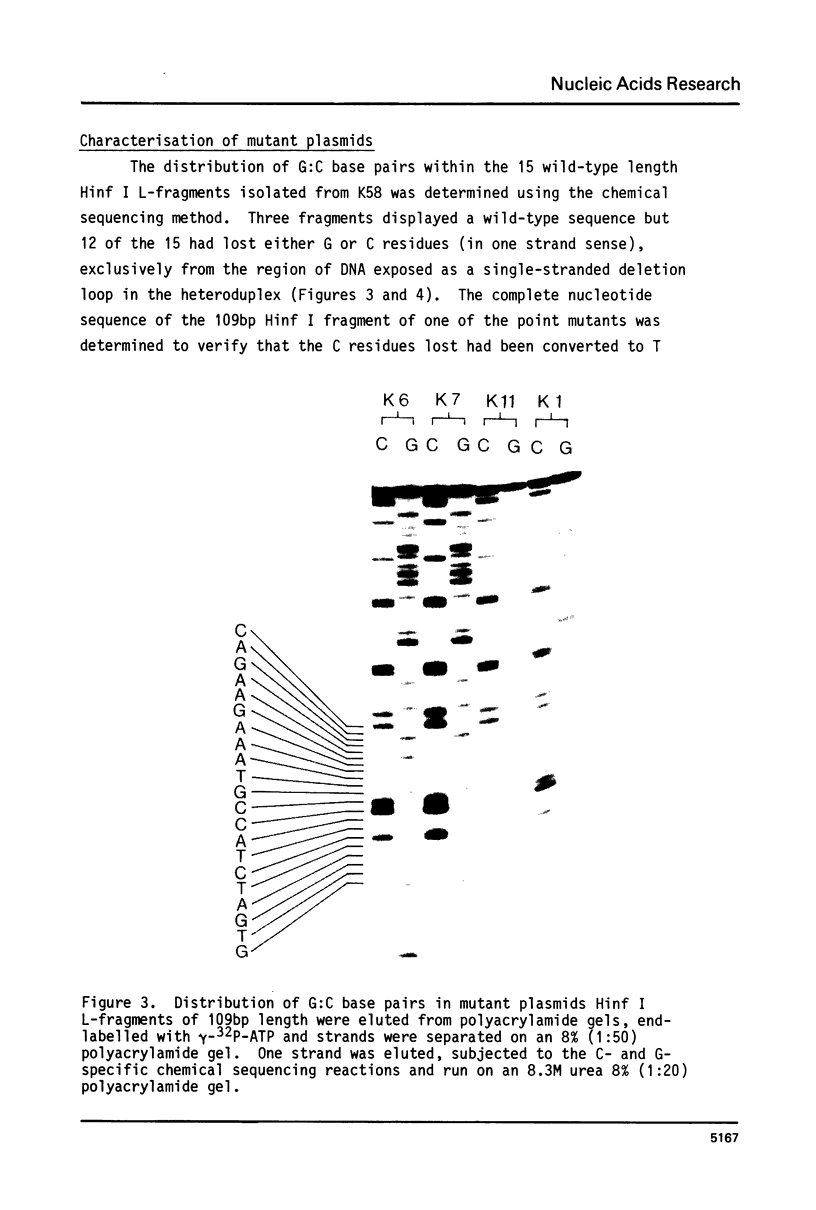
Deletion loop mutagenesis is a new, general method for site-directed mutagenesis that allows point mutations to the introduced within a sequence of DNA defined by a previously isolated deletion mutant. Wild type and deletion mutant DNA are cloned into a bacterial plasmid and each is cleaved with a different single cut restriction enzyme. Heteroduplexes are formed between the two DNAs to produce circular molecules containing a nick in each strand and a single-stranded deletion loop. The deletion loops are mutagenised using sodium bisulphite and the DNA transfected directly into a uracil repair deficient strain of Escherichia coli. Up to half of the resultant clones contain DNA produced by replication of the wild-type length strand and bear mutations exclusively within the target area. An example is given in which a deletion mutant lacking 21 nucleotides from the region coding for SV40 large-T was used. Eight of the possible nine target cytosine residues were mutagenised. The method described is specific, efficient and simple.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrias W. E., Wilschut I. J., Vereijken J. M., Weisbeek P. J., van Arkel G. A. Induction and isolation of mutants in a specific region of gene A of bacteriophage phi chi 174. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Rockstroh P. A., Warner H. R. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants deficient in uracil-DNA glycosylase. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1039-1045.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Chambon P. A rapid and efficient method for region- and strand-specific mutagenesis of cloned DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):433–437. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giza P. E., Schmit D. M., Murr B. L. Region- and strand-specific mutagensis of a recombinant plasmid. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Shewmaker C. K., Jat P., Flavell R. A. Localization of DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Wu R. New rapid methods for DNA sequencing based in exonuclease III digestion followed by repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2065–2084. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayatsu H. Bisulfite modification of nucleic acids and their constituents. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;16:75–124. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60756-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S., Edgell M. H., Gillam S., Jahnke P., Smith M. Mutagenesis at a specific position in a DNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6551–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman I. R., Tye B. K., Nyman P. O. Excision-repair of uracil in DNA: its implications for the discontinuous replication of DNA in vivo and in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):221–230. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA glycosylases, endonucleases for apurinic/apyrimidinic sites, and base excision-repair. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1979;22:135–192. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60800-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Weber H., Meyer F., Weissmann C. Site-directed mutagenesis in DNA: generation of point mutations in cloned beta globin complementary dna at the positions corresponding to amino acids 121 to 123. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Carbon J., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.664-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., DiMaio D., Nathans D. Directed mutagenesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:265–294. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Koshland D., Weinstock G. M., Botstein D. Segment-directed mutagenesis: construction in vitro of point mutations limited to a small predetermined region of a circular DNA molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5375–5379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Nathans D. Local mutagenesis: a method for generating viral mutants with base substitutions in preselected regions of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the Hind-C fragment of simian virus 40 DNA. Comparison of the 5'-untranslated region of wild-type virus and of some deletion Mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., Schaller H. Segment-specific mutagenesis: extensive mutagenesis of a lac promoter/operator element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakour R. A., Loeb L. A. Site-specific mutagenesis by error-directed DNA synthesis. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):708–710. doi: 10.1038/295708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]