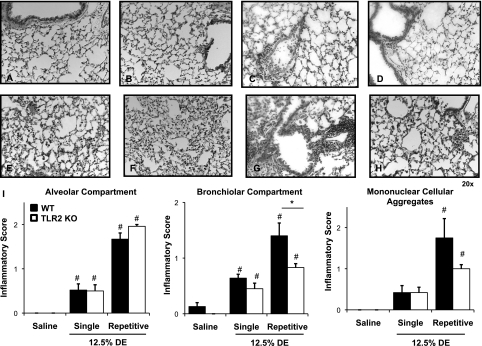
Figure 6.
Reduced lung inflammation in TLR2-deficient mice after intranasal inhalation of DE. Saline-treated WT mice (A) and saline-treated TLR2 KO mice (B) are compared, with mice exposed once ([C] WT and [D] TLR2 KO) and mice exposed repeatedly for 2 weeks ([E and G] WT; [F and H] TLR2 KO) to DE (12.5%). A representative 4- to 5-μm-thick section of one of four to six mice per treatment group is shown at 20× magnification. (E and F) Alveolar compartment inflammation; (G and H) Bronchiolar compartment inflammation after repetitive (2-wk) DE challenge in WT and TLR2 KO mice, respectively. (I) Semiquantitative inflammatory score of lungs after intranasal inhalation of saline and DE (12.5%) after single exposure or repetitive (2-wk) exposure of DE. Semiquantitative distribution of lung alveolar inflammation, bronchiolar inflammation, and mononuclear cellular aggregates in mice (n = 4–6 mice per group). Error bars represent SE. #P < 0.05, significant differences between saline and DE treated; (*P < 0.05, differences between TLR2 KO and WT.