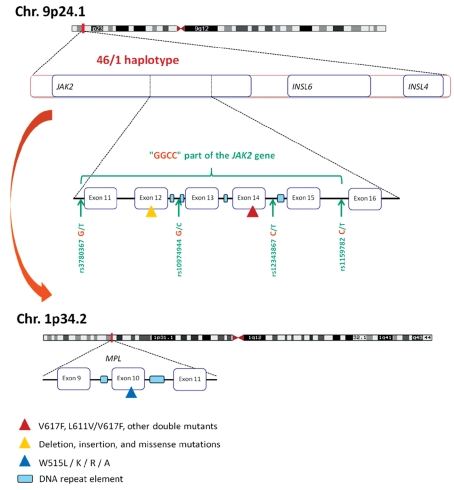
Figure 1.
The 46/1 haplotype associated with a predisposition to mutation in the JAK2 and MPL genes and MPN. The 46/1 haplotype is a 280 Kb-long region of chromosome 9p which includes the entire JAK2, INSL6 and INSL4 genes. Most of the JAK2 mutations detected in MPN are localized in the “GGCC” part of the JAK2 gene, represented in green. The “GGCC” part, which begins in intron 10 and finishes in intron 15 of the JAK2 gene, is characterized by four single nucleotide polymorphisms: rs3780367 in intron 10, rs10974944 in intron 12, rs12343867 in intron 14, and rs1159782 in intron 15. These four single nucleotide polymorphisms are in complete linkage disequilibrium. The “GGCC” part of the 46/1 haplotype includes the most frequently mutated JAK2 exons: exon 14 (mainly the V617F mutation, represented by a red triangle), exon 12 (mutations and deletions are represented by a yellow triangle) and to a lesser degree, exons 13 and 15. In addition, the 46/1 haplotype has been reported to be associated with a predisposition to the acquisition of mutations in exon 10 of the MPL gene, located on a different chromosome. MPL exon 10 mutations are represented by a blue triangle. DNA repeat elements (represented by light blue rectangles) can be found close to JAK2 exons 12–15 and close to MPL exon 10. Such repeat sequences are known to increase the risk of DNA mutation or recombination. The presence of repeat elements being independent of the 46/1 haplotype, the mechanisms that make individuals carrying the 46/1 haplotype at higher risk of JAK2 and MPL mutation and MPN are currently not understood.