Figure 1.
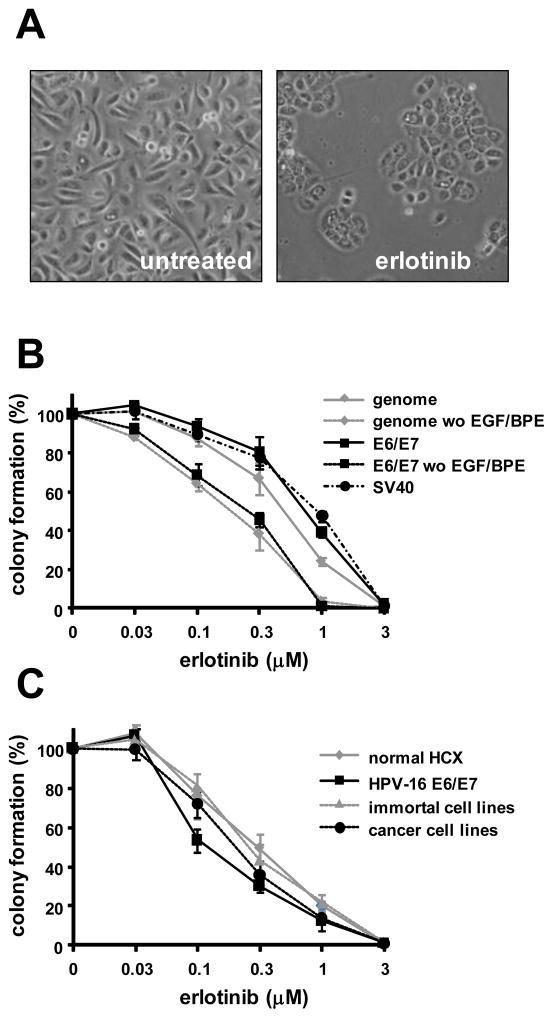
Erlotinib inhibits clonal growth. A. Phase contrast micrographs showing cell growth in KSFM without (left) or with erlotinib (right). B. Erlotinib inhibits colony formation in a dose-dependent manner. Cervical epithelial cells were transfected with the complete HPV-16 genome, SV40 DNA, or infected with retroviruses encoding HPV-16 E6/E7 and then treated with various doses of erlotinib for 10 days in KSFM or KSFM without added EGF and BPE. For each experiment colony number was determined by counting cells in 3 replicate dishes from 3 different donors. C. Erlotinib inhibits colony formation by cells at progressive stages leading to cancer. Three normal cervical cell strains (normal HCX), 3 strains infected with HPV-16 E6/E7 retroviruses, 3 HPV-16-immortal cell lines, and 3 cervical carcinoma cell lines were treated with erlotinib and the mean cloning efficiency was measured. Points represent percent colony formation ± standard deviation in 3 independent experiments.