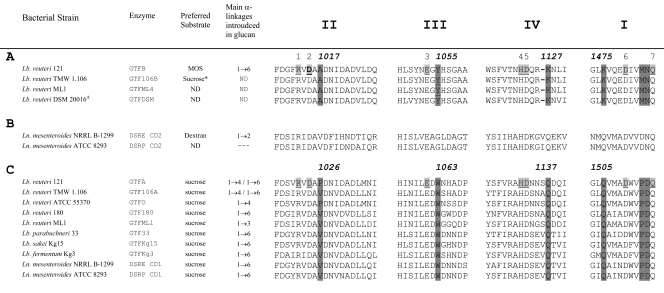
Fig. 2.
Amino acid sequence (http://www.cazy.org) alignment of conserved regions (II, III, IV, and I) in the catalytic domains of (putative) 4,6-α-glucanotransferase enzymes (A), DSRE (5) and DSRP, glucansucrase enzymes containing two catalytic domains (CD1 and CD2) (B), and dextran-, mutan-, alternan-, and reuteransucrase enzymes of lactic acid bacteria (C) (see also references 17 and 23). The seven strictly conserved amino acid residues (indicated by the numbers 1 to 7 above the sequences; underlined and lightly shaded in L. reuteri 121 GTFA and GTFB), with important contributions to the −1 and +1 subsites in glucansucrase enzymes, are also conserved in the 4,6-α-glucanotransferase enzymes. GTFB amino acid D1015 (the putative nucleophilic residue), targeted in this study, is shown in boldface. Dark shading indicates changes in conserved amino acid residues between 4,6-α-glucanotransferases and glucansucrases; the corresponding amino acid numbering is indicated. *, low activity.