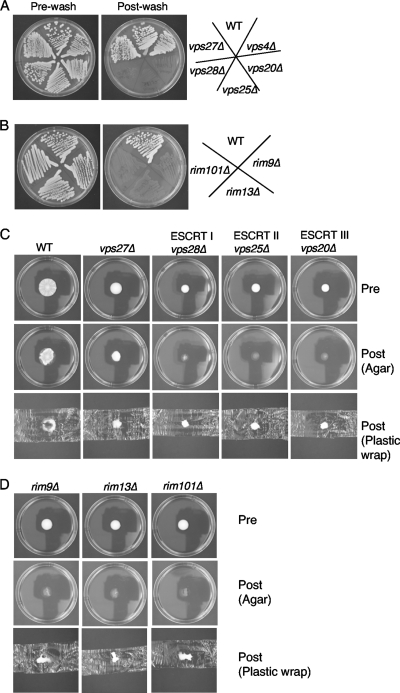
Fig. 1.
Class E vps mutants that affect the Rim101p signaling pathway (class E-1) cause defects in mat formation and invasive growth, but class E vps mutants that do not affect the Rim101p pathway (class E-2) disrupt mat formation but not invasive growth. (A) The class E vps mutants vps27Δ, vps28Δ (ESCRT-I), vps25Δ (ESCRT-II), vps20Δ (ESCRT-III), and vps4Δ were subjected to the invasive growth assay (WT, wild type); (B) members of the Rim101p signaling pathway, rim101Δ, rim9Δ, and rim8Δ, were subjected to the invasive growth assay; (C and D) representative members of the class E-1 and E-2 vps mutants (C) and the Rim101p signal transduction pathway (D) were subjected to the overlay adhesion assay.