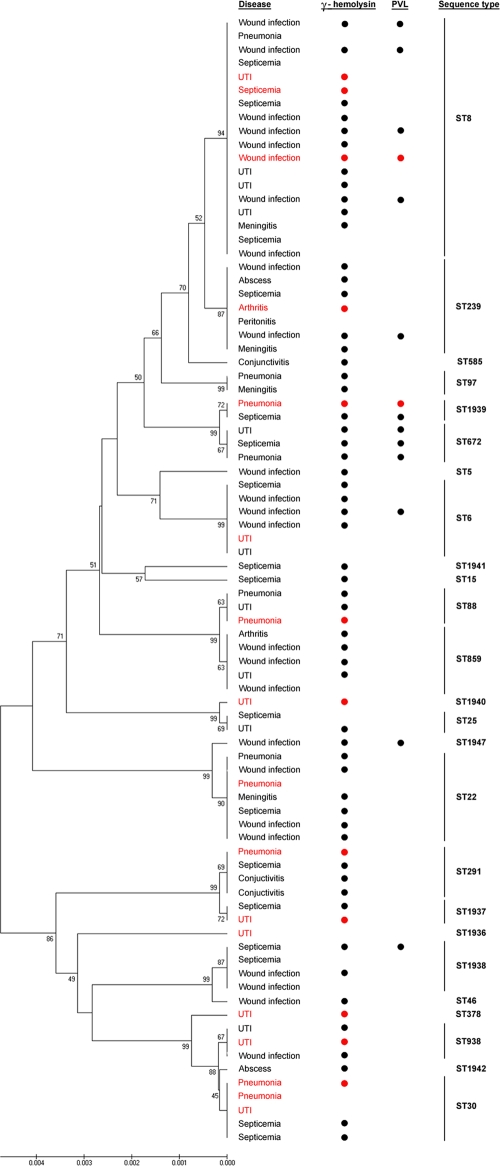
Fig. 1.
Phylogenies of concatenated sequences from the 83 isolates of S. aureus. Each isolate was presented by the type of infection that it caused. Bullets identify isolates that are γ-hemolysin and PVL positive. Vertical bars on the far right identify groups of isolates with the same sequence types. Community-acquired S. aureus isolates are indicated by a red color, while hospital-acquired S. aureus isolates are black. The phylogenetic tree was inferred according to the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean using the matrix of pairwise differences.