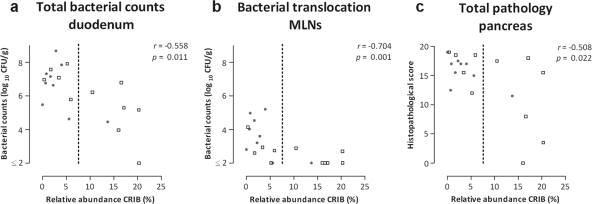
Fig. 4.
Associations between different measures of disease outcome and the relative ileal abundance of CRIB in diseased rats after 7 days of acute pancreatitis. Animals were treated with either placebo (gray dots) or probiotics (squares). Indicated are total bacterial counts in the duodenum (a), bacterial translocation to the MLNs (b), and total pathology of the pancreas (c). The relative abundance of CRIB was determined by qPCR analysis. Bacterial counts are expressed in log10 CFU per gram of sample. Pearson's correlation coefficients are provided, with corresponding P values. The dotted lines indicate the divisions between the samples with a low (<7.5%) or high (>7.5%) relative ileal abundance of CRIB (>7.5%).