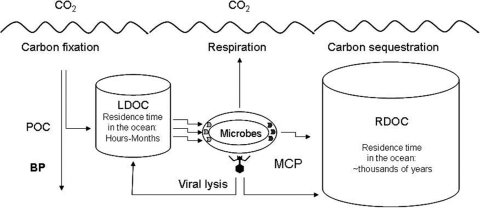
Fig. 1.
Diagram showing the microbial carbon pump (MCP) in the context of carbon cycling in the ocean. LDOC, labile dissolved organic carbon; RDOC, recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon; POC, particulate organic carbon; BP, biological pump, the known carbon-sequestration mechanism which is based on POC sinking from the surface to depths and even the bottom of the ocean. The MCP, a newly proposed mechanism of carbon sequestration, is based on microbial formation of RDOC, which is resistant to biological degradation and persistent in the water column for thousands of years. The major MCP processes includes microbial exudation of RDOC compounds and viral lysis of the host cells that releases partially RDOC compounds. The ellipse shape indicates a microbial cell with importers (left) and exporters (right).