Abstract
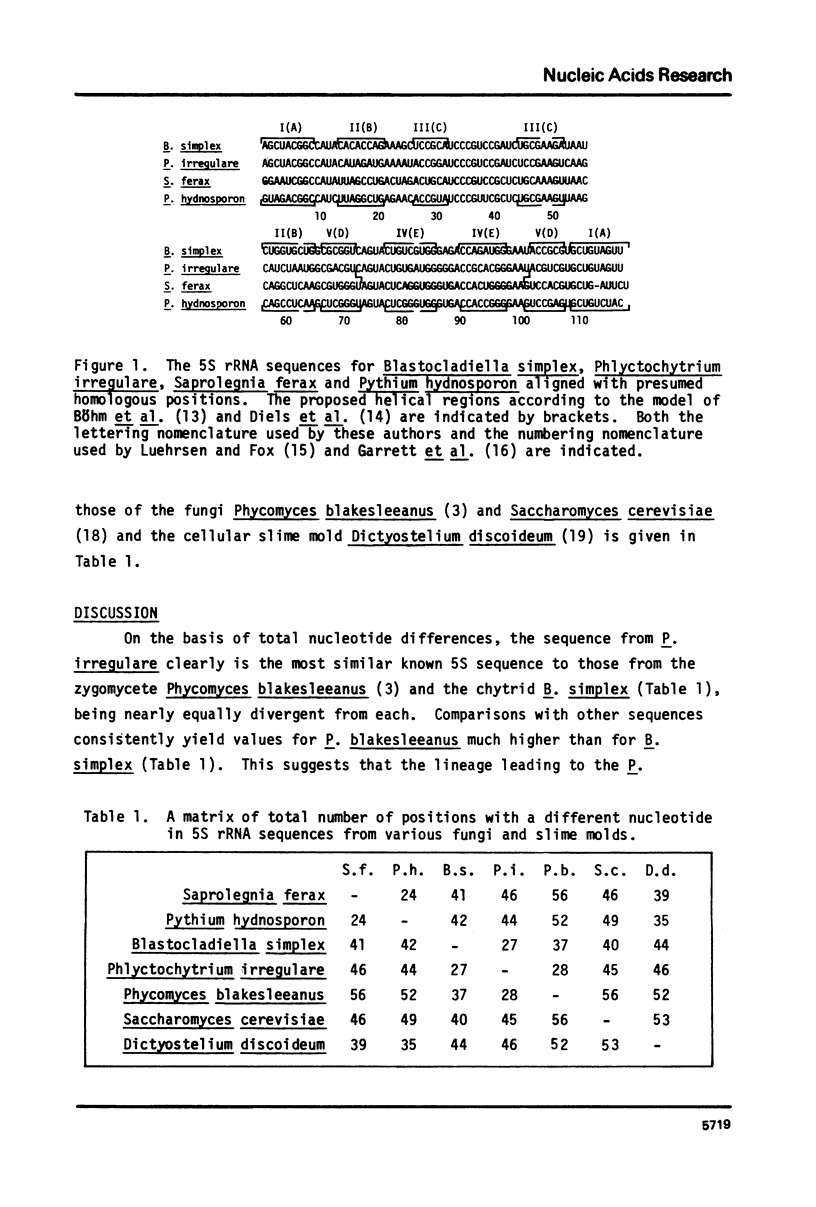
The nucleotide sequences of the 5S rRNAs of the oomycete water molds Saprolegnia ferax and Pythium hydnosporum and of the chytrid water molds Blastocladiella simplex and Phlyctochytrium irregulare were determined by chemical and enzymatic partial degradation of 3' and 5' end-labelled molecules, followed by gel sequence analysis. The two oomycete sequences differed in 24 positions and the two chytrid sequences differed in 27 positions. These pairs differed in a mean of 44 positions. The chytrid sequences clearly most resemble the sequence from the zygomycete Phycomyces, while the oomycete sequences appear to be allied with those from protozoa and slime molds.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Andresini W., Kaufman L., Lyman H. The 5S ribosomal RNA of Euglena gracilis cytoplasmic ribosomes is closely homologous to the 5S RNA of the trypanosomatid protozoa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6627–6633. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diels L., De Baere R., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. The sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA of the crustacean Artemia salina. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5141–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S., Iwabuchi M. The nucleotide sequence of 5S rRNA from a cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5535–5539. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya H., Takemura S. The nucleotide sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA from slime mold Physarum polycephalum. J Biochem. 1981 Dec;90(6):1577–1581. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Fox G. E. Secondary structure of eukaryotic cytoplasmic 5S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2150–2154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LéJohn H. B. Enzyme regulation, lysine pathways and cell wall structures as indicators of major lines of evolution in fungi. Nature. 1971 May 21;231(5299):164–168. doi: 10.1038/231164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Nucleotide sequence of Crithidia fasciculata cytosol 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4911–4917. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Walker T. A., Pace B., Erikson R. L. The nucleotide sequence of chicken 5S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1974;3(2):151–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01796560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker R. H. New concepts of kingdoms or organisms. Evolutionary relations are better represented by new classifications than by the traditional two kingdoms. Science. 1969 Jan 10;163(3863):150–160. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3863.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


