Fig. 7.
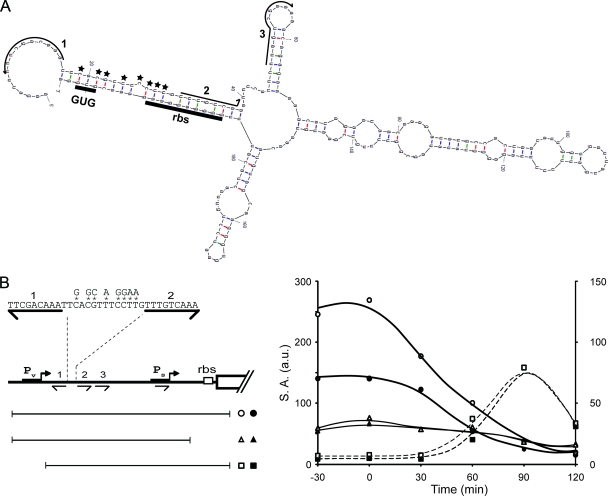
RNA secondary structure impedes translation mRNAs originating from Pv. (A) Secondary structure prediction for the 5′ region of transcripts originating from Pv. RNA sequences corresponding to O1, O2, and O3 are indicated with arrows. The ribosome-binding site (RBS) and initiation codon (GUG) are underlined. Positions of nucleotide substitution mutations are indicated with stars. (B) Expression of spo0A-lacZ fusions integrated at amyE. A typical experiment is presented. The fusions were either translational, containing the full regulatory region (from −305 to +72) (circles) (Abs1019 and Abs1021) or lacking Pv (from −197 to +72) (squares) (Abs988 and Abs957) or were transcriptional, containing the full regulatory region (from −305 to −16) (triangles) (Abs1049 and Abs1050). The fusions either contained the wild-type sequence (black symbols) or were mutants, with the eight nucleotide substitutions indicated in the left panel. Expression of fusions containing the full regulatory region (circles and triangles) were determined in mutant cells lacking σH (sigH) to prevent expression from Ps. Dotted lines correspond to the right axis and continuous lines to the left axis.