Fig. 2.
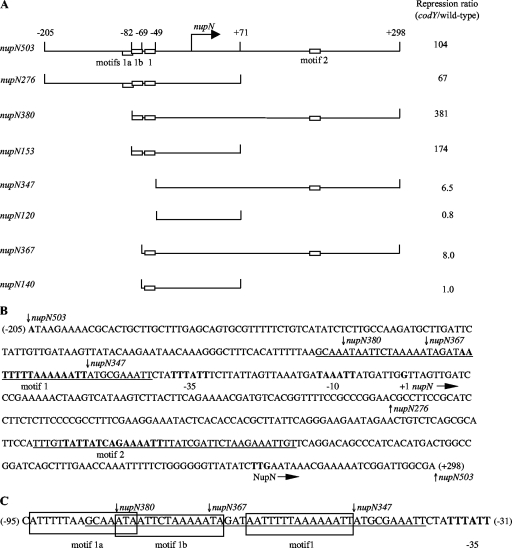
Plasmid maps and the sequence of the nupN regulatory region. (A) Schematic maps of the nupN inserts used to construct lacZ fusions. The location of the transcription start point is indicated by the bent arrow. CodY-binding motifs are shown as rectangles. The coordinates indicate the boundaries of different fusions with respect to the transcription start point. The repression ratio is the ratio of expression values for the corresponding fusions in the codY-null mutant and wild-type strain in the 16-amino-acid-containing medium. (B) Sequence of the coding (nontemplate) strand of the nupN regulatory region. The likely initiation codon, −10 and −35 promoter regions, transcription start site, and CodY-binding motifs 1 and 2 are in boldface. The direction of transcription and translation is indicated by the arrows. The sequences protected by CodY in DNase I footprinting experiments on the template strand of DNA are underlined. The boundaries of DNA fragments used to construct various lacZ fusions are indicated by vertical arrows. The coordinates of the 5′ and 3′ ends of the sequence with respect to the transcription start point are shown in parentheses. Note the incorrect annotation of the nupN initiation codon in older databases. (C) Motifs in the nupN CodY-binding site I. The sequences protected by CodY in DNase I footprinting experiments on the template strand of DNA are underlined. The sequences of motifs 1a, 1b, and 1 are boxed. The −35 promoter region is in boldface. The boundaries of DNA fragments used to construct various lacZ fusions are indicated by vertical arrows. The coordinates of the 5′ and 3′ ends of the sequence with respect to the transcription start point are shown in parentheses.