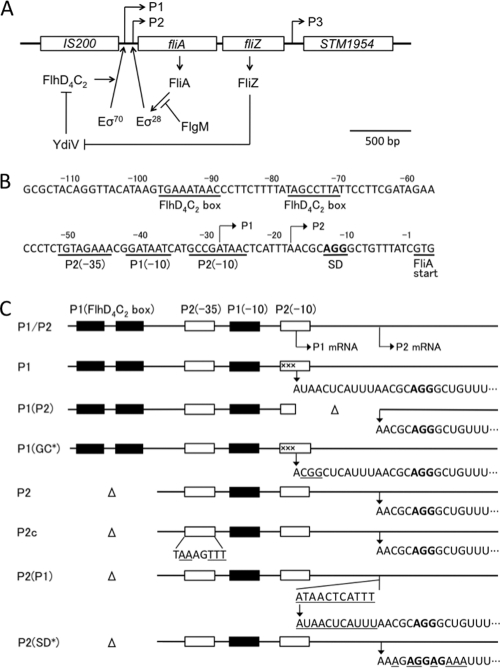
Fig. 1.
Expression control of the fliAZ operon and nucleotide sequence of its regulatory region. (A) The structure of the fliAZ operon on the Salmonella chromosome is drawn with the model of its expression control according to previously published reports (1, 14, 27, 28, 31, 45, 46). STM1954 has also been called fliY (38). (B) The nucleotide sequence of the regulatory region of the fliAZ operon is shown with the translation initiation codon of the fliA gene being numbered 1. Various control signals of the fliA gene are underlined. (C) The structures of the regulatory region of the fliAZ operon in the various mutants constructed in this study are shown with the nucleotide sequences of the 5′ ends of their transcripts. Closed boxes, sequences responsible for the P1 promoter; open boxes, sequences responsible for the P2 promoter. Altered or inserted nucleotides in the mutant constructs are underlined. ×××, 3-nucleotide substitution mutation (GCC to CGT) which inactivates the P2 promoter. SD sequences are written in boldface.