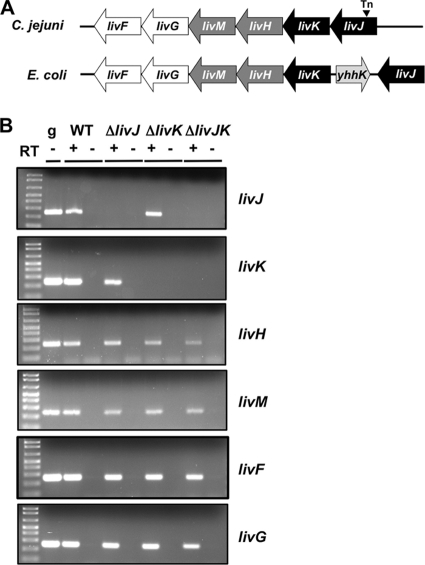
Fig. 1.
Organization of the liv loci of C. jejuni and E. coli and analysis of constructed C. jejuni liv mutants. The LIV locus of C. jejuni 81-176 contains six consecutive genes. In E. coli, livJ is separated from the other liv genes by the gene yhhK (light gray arrow) (1). The genes of the LIV system in these bacteria include livJ and livK (encoding the LIV binding proteins; black arrows), livH and livM (encoding the inner membrane permeases; dark gray arrows), and livG and livF (encoding the cytoplasmic ATPases; white arrows). The triangle indicates the site of the insertion of the signature-tagged Tn in the 81-176 mutant that was previously identified to have a reduced ability to colonize the chick ceca (14). (B) Qualitative reverse transcriptase PCR analysis of expression of liv genes in wild-type (WT) C. jejuni and ΔlivJ, ΔlivK, and ΔlivJK mutants. RNAs from C. jejuni strains were used in reactions with or without reverse transcriptase (RT) to generate cDNA. Each gene was amplified from cDNA using gene-specific primers. A positive control for amplification of each gene was performed by PCR with wild-type C. jejuni 81-176 genomic DNA (g).