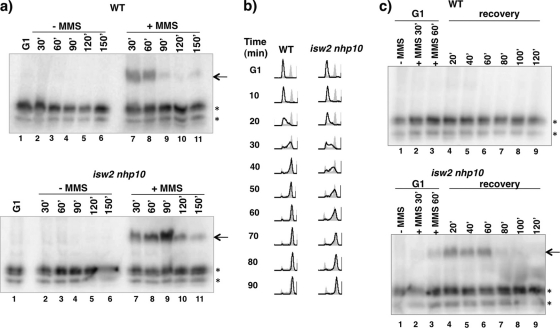
Fig. 2.
Isw2 and Ino80 attenuate S phase checkpoint activity and facilitate efficient checkpoint deactivation during and after MMS treatment. (a) Rad53 ISA assay during MMS treatment. WT and isw2 nhp10 cells were arrested in G1 and released into YPD in the absence or presence of 0.02% (vol/vol) MMS. Cells were harvested during G1 arrest and every 30 min during release until 150 min postrelease. The arrow shows the Rad53 ISA band, and asterisks designate other kinases with ISA activity that served as a loading control. (b) Flow cytometry analysis after transient MMS treatment. WT and isw2 nhp10 cells were arrested in G1 by α-factor treatment. α-Factor was readded for 75 min, and 0.02% (vol/vol) MMS was added 15 min later for a total of 60 min of MMS treatment during G1. Cells were released into S phase in YPD and collected at the indicated time points after release. DNA content was analyzed by flow cytometry (black lines). Gray profiles correspond to the results obtained with reference asynchronous cells collected before G1 arrest. (c) Rad53 ISA assay during recovery from MMS treatment. Cells were harvested before MMS was added, at two time points during MMS treatment in G1, and every 20 min during S phase recovery. The arrow shows the Rad53 ISA band, and asterisks designate other kinases with ISA activity that served as a loading control.