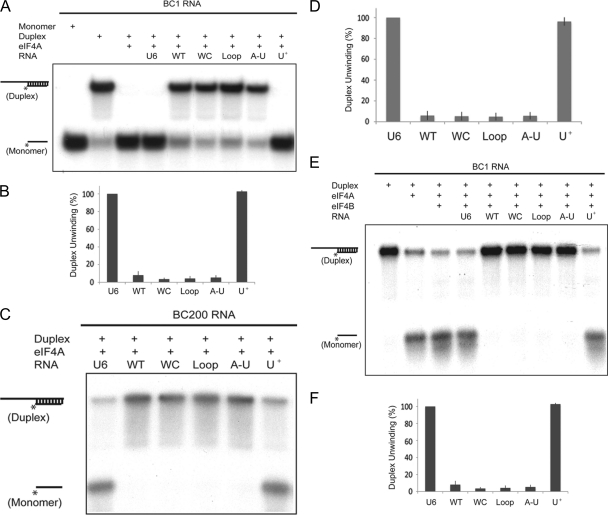
Fig. 5.
The BC RNA A-rich central domains mediate repression of eIF4A helicase activity. RNA duplexes (12/44 nt, 32P-labeled on the 12-nt short strand) were used as helicase substrates in the presence of 1 mM ATP. (A and B) The BC1 RNA central domain mediates repression of eIF4A helicase activity. Labeled RNA monomer and RNA duplexes in the absence of eIF4A were run in the 1st and 2nd lanes, and eIF4A-unwound duplexes were run in the 3rd lane. U6 RNA did not significantly inhibit unwinding (4th lane). WT BC1 RNA inhibited RNA duplex unwinding (5th lane). BC1 RNA C-loop mutants WC, Loop, and A-U (6th to 8th lanes) all inhibited unwinding in a manner indistinguishable from the results for WT BC1 RNA. In contrast, central domain mutant U+ did not inhibit unwinding (9th lane). (B) Quantitative analysis confirmed the above-described results. Error bars show SEM; n = 4, one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001; Tukey post hoc analysis, comparison with U6 RNA, P < 0.001 for WT BC1 RNA and mutants WC, Loop, and A-U and P = 0.970 for mutant U+; comparison with WT BC1 RNA, P < 0.001 for U6 RNA and mutant U+, P = 0.803 for WC, P = 0.891 for Loop, and P = 0.969 for A-U. (C and D) The BC200 RNA central domain mediates repression of eIF4A helicase activity. WT BC200 RNA significantly repressed eIF4A helicase activity (2nd lane) while U6 RNA did not (1st lane). BC200 RNA C-loop mutants WC, Loop, and A-U (3rd to 5th lanes) inhibited eIF4A helicase activity in a manner indistinguishable from the results for WT BC200 RNA. In contrast, central domain mutant U+ (6th lane) did not significantly inhibit duplex unwinding (indistinguishable from the results for U6 RNA in the 1st lane). (D) The above-described results were confirmed by quantitative analysis. Error bars show SEM; n = 4, one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001; Tukey post hoc analysis, comparison with U6 RNA, P < 0.001 for WT BC200 RNA and mutants WC, Loop, and A-U and P = 0.976 for mutant U+; comparison with WT BC200 RNA, P < 0.001 for U6 RNA and mutant U+ and P = 1.0 for mutants WC, Loop, and A-U. (E and F) eIF4B-stimulated eIF4A helicase activity is repressed by BC1 RNA via its central A-rich domain. Labeled RNA duplexes in the absence of protein were run in the 1st lane. eIF4A (2nd lane) or eIF4A and eIF4B in combination (3rd lane) were added. WT BC1 RNA and BC1 RNA C-loop mutants WC, Loop, and A-U inhibited RNA duplex unwinding (5th to 8th lanes) in a manner indistinguishable from each other. In contrast, neither BC1 RNA central domain mutant U+ (9th lane) nor U6 RNA (4th lane) inhibited unwinding. (F) Quantitative analysis confirmed the above-described results. Error bars show SEM; n = 4, one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001; Tukey post hoc analysis, comparison with U6 RNA, P < 0.001 for WT BC1 RNA and C-loop mutants WC, Loop, and A-U and P = 0.998 for mutant U+; comparison with WT BC1 RNA, P < 0.001 for U6 RNA and mutant U+ and P = 1.0 for mutants WC, Loop, and A-U.