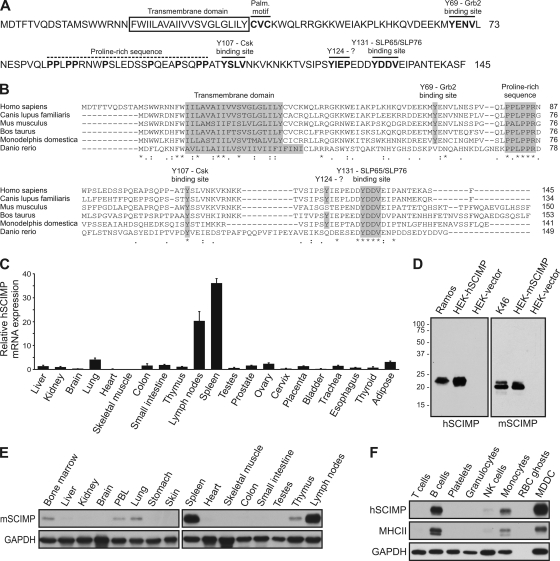
Fig. 1.
SCIMP is a transmembrane adaptor protein expressed in antigen-presenting cells. (A) Sequence of human SCIMP. Positions of the transmembrane domain, palmitoylation motif, proline-rich sequence, and predicted Grb2, Csk, and SLP65/SLP76 binding sites are indicated. (B) Comparison of SCIMP sequences from human (Homo sapiens), dog (Canis lupus familiaris), mouse (Mus musculus), cattle (Bos taurus), opossum (Monodelphis domestica), and zebrafish (Danio rerio). The transmembrane domain, highly conserved part of the proline-rich sequence and SLP65/SLP76 binding motif, as well as other conserved tyrosine residues, are highlighted, and positions of corresponding tyrosines in human sequence are marked. Respective GenBank accession numbers are: NP_996986, XP_849038, NP_001038991, XP_001251000, and XP_001377777. Sequence of Danio rerio SCIMP was deduced from two overlapping expressed sequence tag (EST) sequences, EB765140 and EB768085 (C) RT-qPCR analysis of SCIMP mRNA expression in human tissues. Average expression in all tissues corresponds to value 1 on the vertical axis. Data are presented as the mean of four experiments (± SD). (D) Western blot reactivity of anti-SCIMP antibodies on lysates from nontransfected B cell lines Ramos (human) and K46 (murine) or from HEK293 cells transfected with human (hSCIMP) or murine SCIMP (mSCIMP) constructs or empty vector. hSCIMP was stained with mouse monoclonal antibody (NVL-07) and mSCIMP with rabbit antiserum to mSCIMP. (E) SCIMP expression in mouse tissues and peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs), analyzed by immunoblotting. (F) SCIMP and MHC-II expression in isolated human blood leukocyte subsets and in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDC), analyzed by immunoblotting. GAPDH serves as a loading control; data are representatives of two independent experiments (E and F).