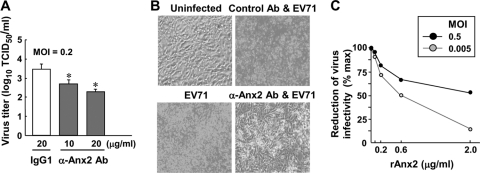
Fig. 4.
Expression of Anx2 on the cell surface impacts the infectivity of EV71. RD cells (1 × 105) were pretreated with an anti-Anx2 antibody (Ab) (10 or 20 μg/ml) or a mouse IgG1 isotype control antibody (20 μg/ml) for 1 h at 37°C before infection with EV71 (MOI, 0.2). (A) At 42 h postinfection, the virus yield was determined by a TCID50 assay (means ± SE for four experiments). Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) between anti-Anx2 antibody-pretreated and IgG1-pretreated RD cells. (B) At 42 h postinfection, the typical CPE of EV71 infection was viewed under a visible-light phase-contrast microscope, showing representative fields of the RD cells alone (Uninfected) or of EV71 infecting either untreated RD cells, anti-Anx2 antibody-pretreated cells, or control IgG1-pretreated cells. (C) Infectivity of EV71 pretreated with soluble rAnx2. EV71 was pretreated with various doses of rAnx2 at 37°C for 1 h prior to infection of RD cells (2 ×105 cells). The total virus yield at 72 h postinfection was determined by a TCID50 assay by using quintuplet wells for each concentration point and log10 dilution of the virus. The virus titer in cells infected with EV71 but not pretreated with rAnx2 was used as a reference (100%) to calculate the percentages of reduction in the TCID50 for the rAnx2-pretreated groups.