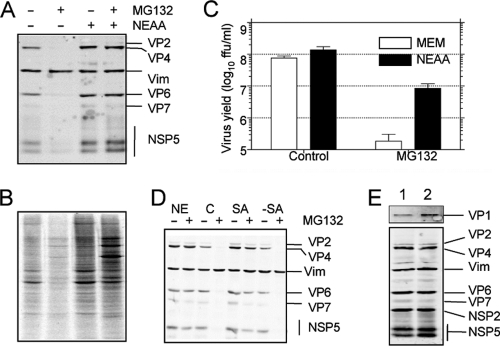
Fig. 3.
The effect of the proteasome inhibitor MG132 on protein synthesis is reversed by addition of nonessential amino acids, but the effect on the yield of progeny virus is not. MA104 cells infected with rotavirus RRV (A) or uninfected (B) were incubated for 12 h in the presence or absence of 10 μM MG132 and 100 μM each NEAA, as indicated. In panel A, the viral proteins were detected by Western blotting, and vimentin (Vim) was used as a loading control. In panel B, during the last hour of incubation, 25 μCi/ml of Easy Tag EXPRESS-35S labeling mix was added; the cells were then washed with PBS and lysed with Laemmli sample buffer. The proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography. (C) Cells in 96-well plates were infected at an MOI of 3, and at 12 hpi, the cells were lysed by two freeze-thaw cycles, and the viral titer was determined by an immunoperoxidase assay. Data represent the arithmetic means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. (D) MA104 cells were infected with rotavirus RRV at an MOI of 3 and incubated in MEM plus NEAA (NE), MEM alone as control (C), MEM plus 100 μM serine and asparagine (SA), or NEAA without serine and asparagine (−SA) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 10 μM MG132. At 12 hpi, the viral proteins were detected by Western blotting. Vimentin (Vim) was used as loading control. (E) MA104 cells were infected at an MOI of 3 and incubated by 8 h in MEM plus NEAA in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of 10 μM MG132. The cells were lysed in Laemmli sample buffer, and the proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using polyclonal antibodies to VP1 (upper panel) or a mixture of sera containing antibodies to purified rotavirus particles, vimentin, NSP2, and NSP5 (lower panel).