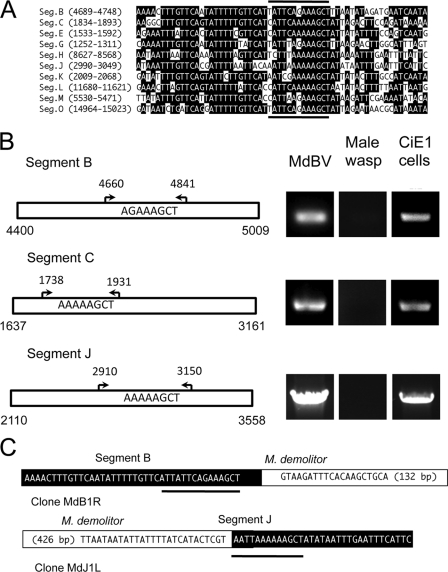
Fig. 4.
A wasp excision/integration motif (WIM) identifies the site of integration of MdBV genomic segments B, C, and J in M. demolitor but not CiE1 cells. (A) Alignment of the predicted WIM on selected MdBV genomic segments. The location of the motif on each segment is indicated at the left. Identical nucleotides are indicated in black. The dark lines above and below the alignment indicate the predicted sites of integration of the corresponding proviral DNA in M. demolitor. (B) Outcome of PCR-based integration assays. Schematics to the left show larger domains on segments B, C, and J where the predicted WIM is located. Arrows and corresponding nucleotides identify the locations of flanking primers used in PCR-based integration assays. To the right of each schematic are the PCR products generated using these primers and DNA from MdBV, adult male M. demolitor, or CiE1 cells infected 21 days earlier with MdBV as a template. (C) Schematics illustrating the right segment B-M. demolitor junction sequence and left segment J-M. demolitor junction sequence cloned by inverse PCR. The MdBV sequence is highlighted in black, and the M. demolitor genomic sequence is highlighted in white. Note that the right boundary border for segment B is identified by the tetramer AGCT, while the right boundary for segment J is identified by the tetramer AATT, as shown by the black underlining in panel A. The cloned and analyzed M. demolitor sequence flanking segment B is 132 bp, while the sequence for segment J is 426 bp.