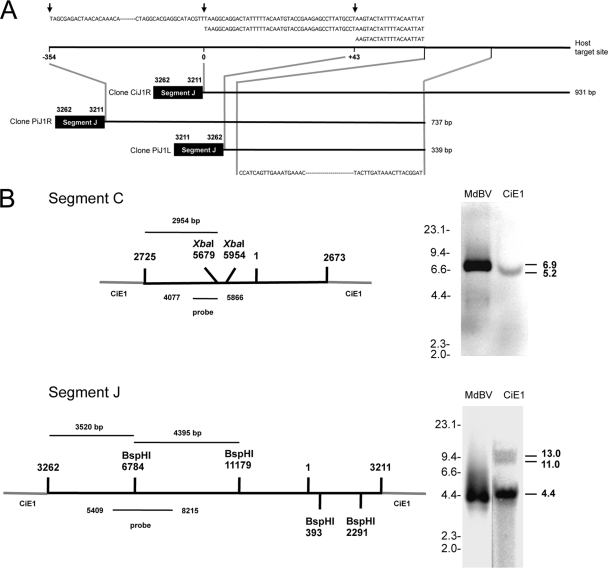
Fig. 7.
Integration of MdBV genomic DNAs is nonrandom. (A) Schematic showing that segment J-host junction clones CiJ1R (931 bp), PiJ1R (737 bp), and PiJ1L (339 bp) integrate into the same target site in CiE1 cells and P. includens. The integration of segment J from clone CiJ1R is shown at position 0 in the host target site. Segment J from clone PiJ1R is inserted at position −354, while segment J from clone PiJ1L is inserted at position +43. Above each clone is the sequence of the deduced host target site, with arrows indicating where each copy of segment J integrated. Below each clone is the region in each clone that was fully identical. (B) Southern blot analysis of MdBV and CiE1 genomic DNAs probed with a segment C-specific (above) or segment J-specific (below) probe. The schematics at the left show segments C and J integrated into CiE1 genomic DNA, as determined by the sequencing of junction clones (Fig. 5 and 6). XbaI (segment C) and BspHI (segment J) sites are indicated, as is the site within each segment that corresponds to the probes that we synthesized. At the right are Southern blots of XbaI-digested MdBV and CiE1 genomic DNAs hybridized with the segment C probe (above) or BspHI-digested MdBV and CiE1 genomic DNAs hybridized with the segment J probe (below). Size markers (kb) are indicated to the left of each blot, while the estimated sizes (kb) of the fragments recognized by each probe are indicated at the right.