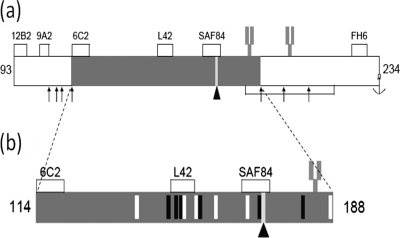
Fig. 3.
Postulated PrPres polypeptide fragment generated by specific Lys-C cleavage. (a) Mature ovine PrP extending from amino acids 25 to 234. The lysine residues which are cleaved following treatment with Lys-C are indicated by arrows. (b) Magnified region of the polypeptide fragment from codons 114 to 188 obtained after Lys-C cleavage of recombinant PrP and scrapie brain-derived PrPres. White vertical bars, 6 basic arginine (R) or lysine (K) residues; black vertical bars, the 6 acidic glutamic acid (E) and aspartic acid (D) amino acid residues; bar marked by an arrowhead, the polymorphic 171 codon that is either a neutral glutamine (Q) or a basic arginine (R). Asparagine at position 184 and 200 can be glycosylated (fork-like structure). The accumulated charge differences between the Lys-C-generated fragments are 0 for the 171Q allele and +1 for the 171R allele. The antibody binding sites for MAbs 12B2, 9A2, 6C2, L42, SAF84, and FH6 are displayed.