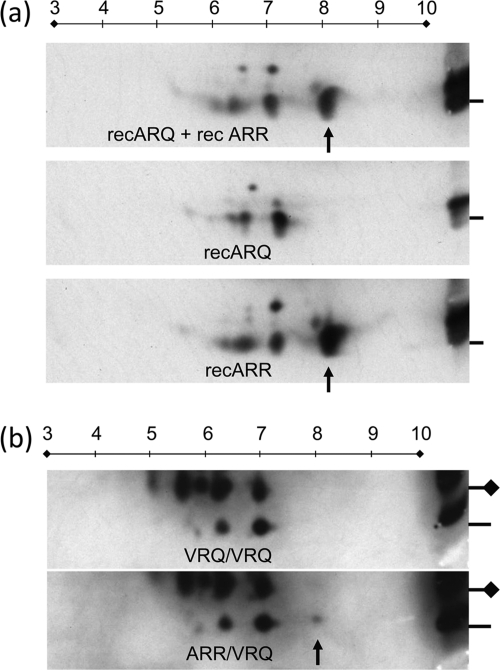
Fig. 6.
Separation based on charge and molecular mass by 2D electrophoresis. The 114-188PrP polypeptide fragments generated by Lys-C cleavage are shown. (a) Result obtained with 171Q and 171R recPrP applied as a mixture or separately (only Lys-C digestion was applied); (b) result obtained with VRQ/VRQ and ARR/VRQ scrapie PrPres (PK and subsequent Lys-C digestion were applied). In panel a, only the 171R fragment shows a dominant L42-positive protein spot at pI 8 (arrow) which was not reactive with the 171Q-dependent antibody SAF84 (data not shown). The reference samples in panels a and b, shown on the right, contain the respective recombinant PrP and sheep samples mixed with molecular mass markers and were run only in the vertical 1D dimension. In panel b, the lines on the right refer to the 6-kDa markers (coinciding with the monoglycosylated 114-188PrPres fragment), and the lines with diamonds indicate the migration positions of the glycosylated 114-188PrPres fragment at 14 kDa. Applied amounts for 1D and 2D analyses were 165 and 330 ng of recombinant PrP, respectively, in panel a and 0.5 and 2.5 mg TEs of brain stem tissue, respectively, in panel b. The MAb L42 concentration was 0.1 μg/ml. In five out of eight cases, only the ARR/VRQ isolates exhibited a faint spot at pI 8 (arrow), which was probably also present at the glycosylated position but too faint for detection due to microheterogeneity of sugar chains. Numbers on lines above the panels indicate isoeletric points.