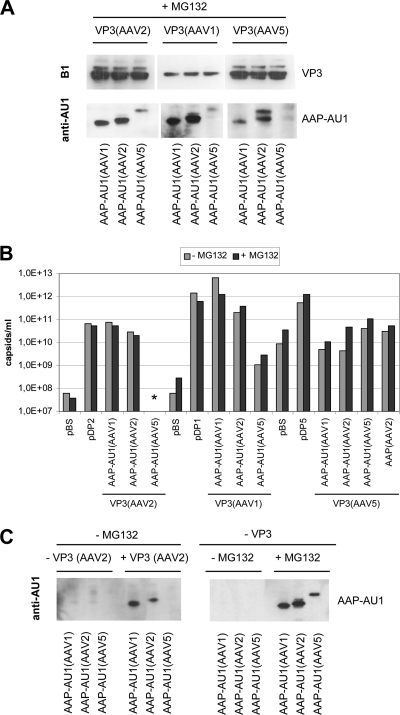
Fig. 9.
Comparison of VP3 capsid assembly activated by AAP derived from AAV1, AAV2, or AAV5 after incubating cells with MG 132. (A) Western blot analysis of VP3 protein expression using MAb B1. AAP-AU1 expression was monitored by using MAb anti-AU1. Transfected cells were incubated with MG132. Arrowheads indicate AAP-specific signals. (B) Capsid formation was quantified by ELISAs based on MAb A20 (AAV2), ADK1 (AAV1), or ADK5 (AAV5). ELISA results are shown as the averages of two independent experiments in the presence of MG132 in comparison to a single experiment without MG132 incubation. Detection limit: A20 ELISA, 5 × 107 capsids/ml; ADK1 ELISA, 5 × 108 capsids/ml; ADK5 ELISA, 2 × 109 capsids/ml. (C) Western blot analysis of AAP-AU1 expression using MAb anti-AU1. The left panel shows AAP expression in the absence or presence of coexpressed VP3 of AAV2, without MG132. The right panel shows AAP expression with or without MG132 incubation of transfected cells in the absence of coexpressed VP3 protein.