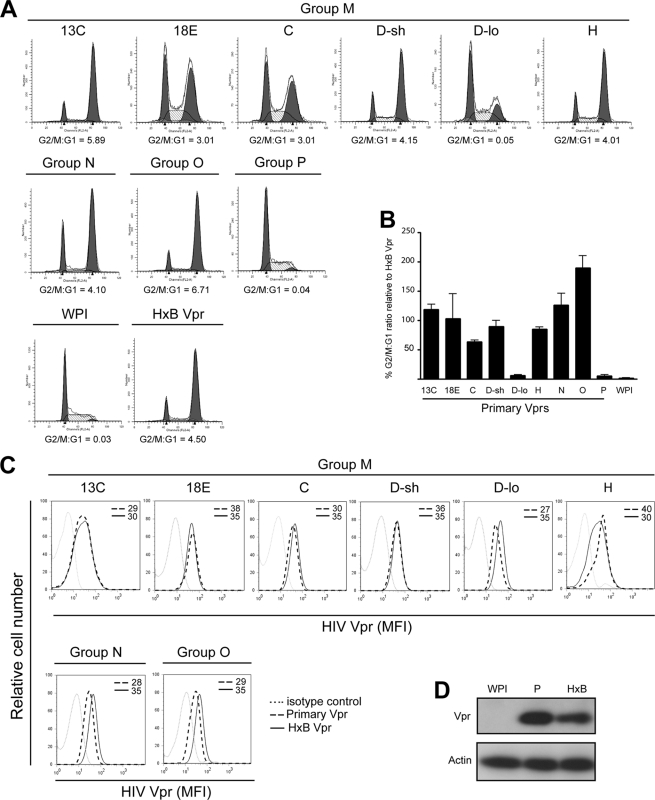
Fig. 2.
Most HIV-1 primary Vpr variants can efficiently induce a G2 cell cycle arrest in T cells. CEM.NKR T cells were transduced with GFP-marked lentiviral vectors expressing Vpr (primary laboratory-adapted [HxB]) or not expressing Vpr (WPI). (A and B) GFP+ cells were sorted and analyzed for cell cycle profiles by flow cytometry. Proportions of cells in G1 and G2 phases were enumerated using the ModFit mathematical model. (A) Representative results from one experiment. (B) Compilation of 3 experiments in which mean G2/G1 ratios ± standard deviations (SD) for primary Vprs were expressed as percentages of that obtained for HxB Vpr. (C) CEM cells were also stained with anti-Vpr MAb (8D1) and analyzed by flow cytometry for Vpr expression in GFP+ cells. MFI values were obtained after subtraction of signals given by cells stained with a relevant isotype control antibody. Shown are data representative of 3 experiments. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with lentiviral vectors expressing no Vpr (WPI), Vpr P, or HxB Vpr and assessed for Vpr expression by Western blotting using anti-Vpr pAb.