Figure 3.
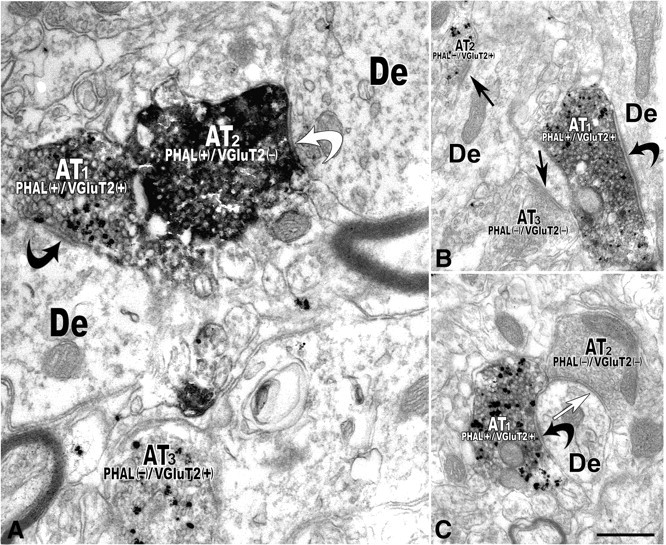
Electron micrographs reveal PHA-L-labeled axon terminals that contain VGluT2 immunolabeling establishing asymmetric synapses on dendrites of local VTA neurons (double immunoelectron microscopy). A, Axon terminal (AT1) containing PHA-L (immunoperoxidase product) and VGluT2 (immunogold-silver particles). PHAL(+)/VGluT2(+) axon terminal makes an asymmetric synapse (black curved arrow) with a dendrite (De). The axon terminal (AT2) containing PHA-L but lacking VGluT2 labeling [PHAL(+)/VGluT2(−)] forms a symmetric synapse (white curved arrow) with a dendrite (De). Note a third axon terminal (AT3) lacking PHA-L but containing VGluT2 [PHAL(−)/VGluT2(+)]. B, A PHA (+)/VGluT2(+) axon terminal (AT1) makes an asymmetric synapse (curved black arrow) with a dendrite (De). A VGluT2-positive terminal (AT2) lacking PHA-L [PHAL(−)/VGluT2(+)] makes an asymmetric synapse (black straight arrow) with a dendrite. An axon terminal (AT3) lacking both PHA-L and VGluT2 [PHAL(−)/VGluT2(−)] makes an asymmetric synapse (black straight arrow) with a dendrite. C, PHA-L(+) and VGluT2(+) axon terminal (AT1) establishes an asymmetric synapse (black curved arrow) with a dendrite (De) receiving a PHA-L and VGluT2-immunonegative [PHAL(−)/VGluT2(−)] axon terminal (AT2) forming a symmetric synapse (white straight arrow). Scale bar (in C): 0.5 μm for A; 0.4 μm for B and C.
