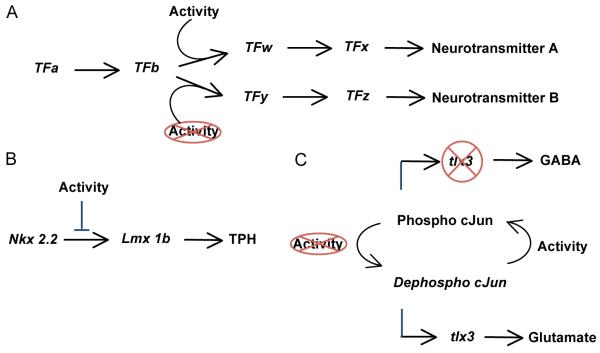
Figure 2. Activity-dependent modulation of transcription factor expression.
A. Cascades of transcription factors (TF) drive the expression of the enzymes and transporters required to specify neurotransmitter phenotype (A, B). Perturbations of activity influence the expression or activity of some (TFw,y) but not all (TFa,b) transcription factors. Activity-dependent transcription factors have been identified as phenotypic checkpoints (Ben-Ari and Spitzer, 2010). B. In the hindbrain, the influence of the frequency of intracellular calcium transients on the cascade of transcription factors leading to the serotonergic phenotype is downstream of Nkx2.2 and upstream of Lmx1b. Activity-dependent expression of Lxm1b regulates the serotonergic phenotype. C. In the spinal cord, the frequency of intracellular calcium transients determines the phosphorylation state of cJun, which in turn regulates the activation of tlx3. The subsequent changes in tlx3 expression promote the choice of fate toward the GABAergic or the glutamatergic phenotype.