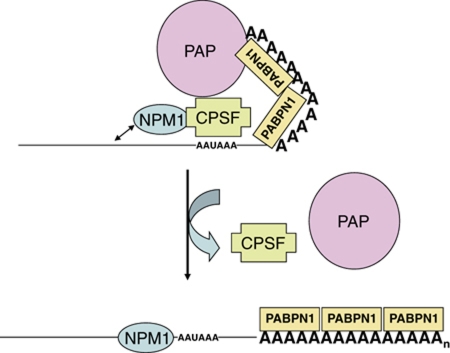
Figure 7.
Model for the regulation of poly(A) tail length by NPM1. NPM1 is directly associated with CPSF-160 which influences poly(A) polymerase activity on the growing tail in conjunction with the poly(A) binding processivity factor PABPN1. The propensity for NPM1 to bind nearby nucleic acids possibly places an additional strain on the CPSF-160 interactions with PAP and PABPN1, perhaps helping the complex dissociate when the poly(A) tail reaches a specific size. In the absence of the constraints imposed by NPM1 interaction, the CPSF−PAP−PABPN1 complex allows for additional rounds of poly(A) synthesis on the growing tail.