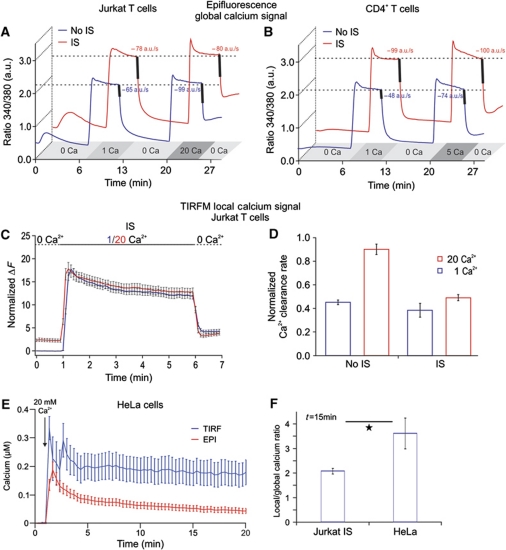
Figure 6.
Formation of the IS reduces Ca2+ microdomain-dependent modulation of PMCA activity in Jurkat T cells. (A) Average of [Ca2+]i responses of so-called iso-cells induced by 1 or 20 mM extracellular Ca2+ solutions in Jurkat T cells. The averages of Ca2+ clearance rates following [Ca2+]i elevation, indicated by the thick lines, were calculated from the dRatio (340/380)/dt slopes over 10 s periods following [Ca2+]o removal (n (No IS)=180, P<0.001; n (IS)=60, P=0.76). (B) Same experiments and analysis as in (A) only with human CD4+ T cells in the presence of 1 or 5 mM extracellular Ca2+ solutions to avoid saturation of the system (n (No IS)=253, P<0.001; n (IS)=176, P=0.6). (C, D) Same experimental design and analysis as in (A) only with TIRFM (n (IS)=18, n (No IS)=50). (E) Global (red trace) and local (blue trace) Ca2+ signals of Fluo-5F-loaded HeLa cells in response to TG stimulation in the presence of 20 mM extracellular Ca2+ solution. Global Ca2+ signals were measured by epifluorescence while local signals were obtained by TIRFM in the same cells. (F) Ratio between the local and global Ca2+ response at 15 min after stimulation with TG in HeLa cells or with TG plus IS in Jurkat T cells. HeLa data were obtained from two independent experiments (n=12, P=0.037). Jurkat T-cell data were taken from experiments shown in Figure 4C and D.