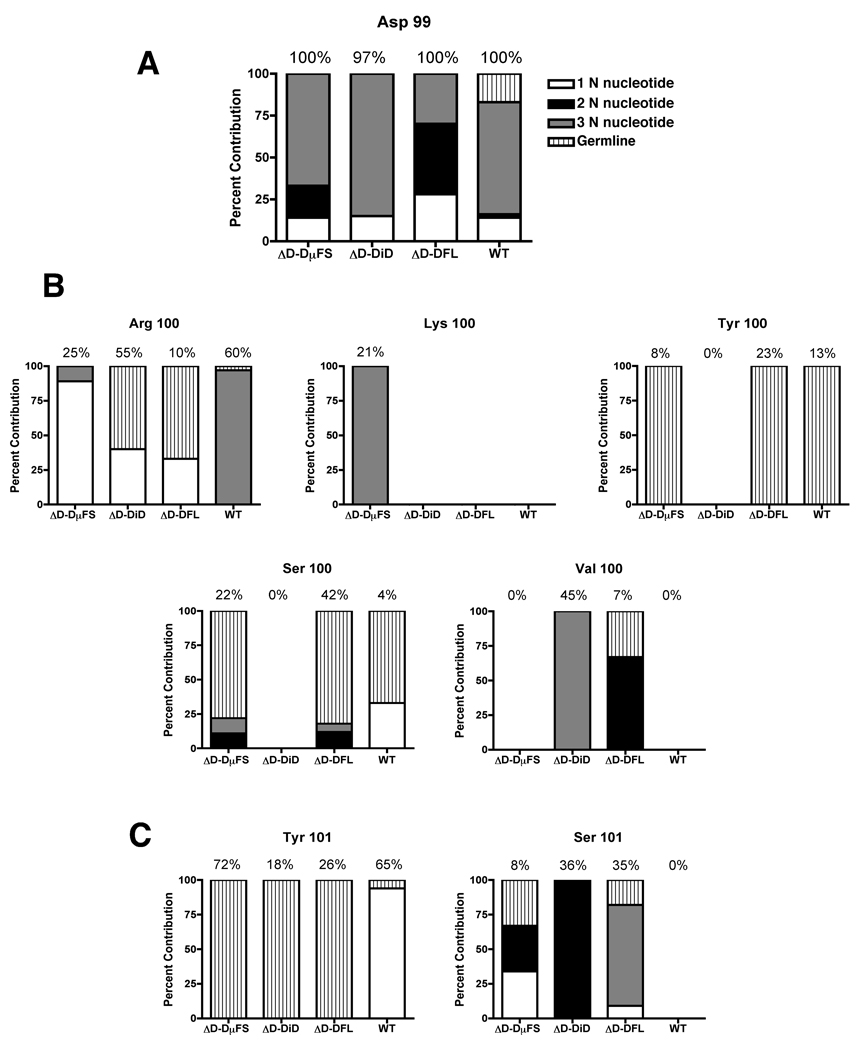
Figure 4. Contribution of N-addition in generating crucial amino acids in CDR-H3 sequences from ΔD-DµFS, ΔD-DiD, ΔD-DFL and WT mice.
The numbers indicate the number of nucleotides that are non-germline (N-nucleotides) that encode for (A) aspartic acid at position 99, (B) arginine, lysine, valine, tyrosine and serine at position 100, (C) tyrosine and serine at position 101 as well as the nucleotides that are germline DH or JH. All are shown as percent of total sequences. Percent usage of each amino acids for each mouse strain is shown on top of each bar.