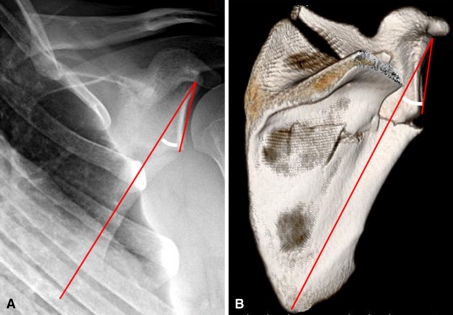
Fig. 4A–B.
Measurement of the GPA on (A) a true AP radiograph and (B) a PA 3D CT scan of the shoulder is demonstrated. A line is drawn from the inferior pole of the glenoid fossa up to the superior pole. Another line is drawn from the superior pole of the glenoid fossa down through the inferior-most angle of the scapula body. The angle formed by these two intersecting lines represents the GPA. Normal GPAs range from 30° to 45° [6]. GPA = glenopolar angle; 3D = three-dimensional.