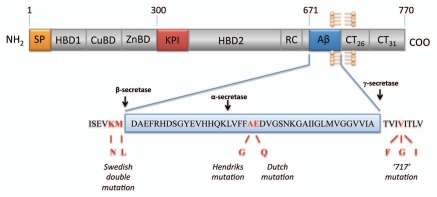
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of APP consisting of a large extracellular domain, a hydrophobic transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus. The protein is proteolytically processed by different secretases via amyloidgenic and non-amyloidgenic proceeding pathways which either releases the Aβ peptide (cleaved by β- and γ-secretase) or precludes Aβ formation (cleaved by α-secretase).