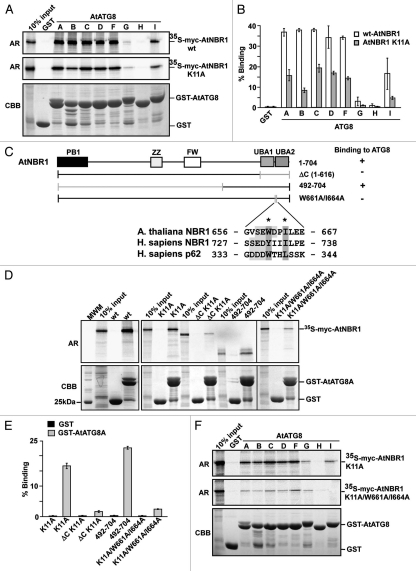
Figure 4.
AtNBR1 binds to Arabidopsis ATG8 family proteins via a LIR-motif located between the twin UBA domains. (A) GST pull-down assays using in vitro translated 35S-labeled myc-AtNBR1 (polymeric and monomeric K11A mutants) and immobilized GST or GST-ATG8 (indicated isoforms) constructs. Precipitated proteins were detected by autoradiography. (B) Quantitative representation of the interaction data shown in (B) (polymeric and monomeric AtNBR1). Y-axis values are set to percent total binding protein; (input/pulldown) × 100. (C) Constructs used and a summary of GST pull-down assays between full-length ATG8A fused to GST and deletion mutants of AtNBR1 (upper part). The lower part shows an alignment of the LIR in AtNBR1 to the corresponding sequences in human p62 and NBR1. The W661 and I664 residues mutated to A are indicated with asterisks. (D) GST pull-down assays using in vitro translated 35S-labeled myc-AtNBR1 (indicated deletions and mutations) and GST or indicated GST-ATG8A constructs. Precipitated proteins were detected by autoradiography. (E) Quantitative representation of the interaction data shown in (B). (F) GST pull-down assays using in vitro translated 35S-labeled, monomeric (K11A mutant) myc-AtNBR1 (indicated mutations) and immobilized GST or indicated GST-ATG8 (indicated isoforms) constructs. Precipitated proteins were detected by autoradiography. Results in (B and E) are mean values of three independent experiments with standard deviations indicated as bars.