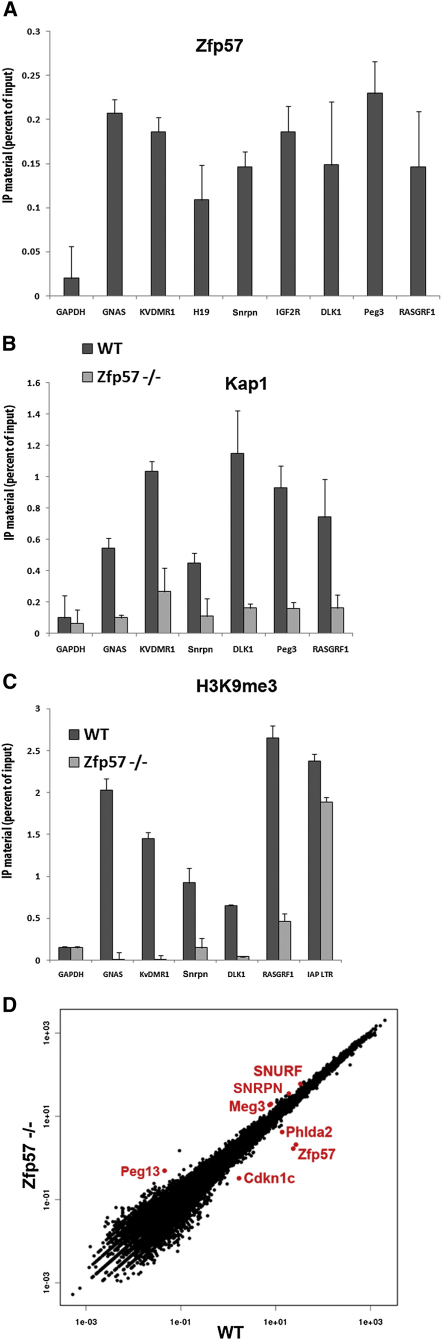
Figure 2.
KAP1 ICR Recruitment in Embryonic Stem Cells Requires ZFP57
(A) ZFP57 binds to ICRs. HA-specific ChIP in ES cells expressing a HA-tagged ZFP57 protein, using primers specific for indicated genomic sequences. Error bars indicate standard deviation, and the difference between Gapdh locus and ICRs is always significant (p < 0.01, n = 3).
(B) No KAP1 ICR recruitment in the absence of ZFP57. Same analysis as in (A), in control and Zfp57 knockout ES cells expressing a HA-tagged form of KAP1. Error bars indicates standard deviation, error bars indicate standard deviation, and the difference between control and Zfp57−/− cells is always significant (p < 0.01, n = 3), except for the Gapdh locus.
(C) H3K9me3 is lost at ICRs in Zfp57-defective ES cells. Same analysis as in (B), using an antibody specific for this chromatin mark. Error bars indicates standard deviation, error bars indicate standard deviation, and the difference between control and Zfp57−/− cells is always significant (p < 0.01, n = 3), except for the Gapdh and IAP LTR loci.
(D) Transcriptional deregulation of several imprinted genes in Zfp57 knockout ES cells. Scatter plot showing the gene expression data extracted from RNA-seq analysis; highlighted in red are Zpf57 and imprinted genes that are most markedly affected. Error bars indicate standard deviation. KV, KvDMR1 ICR.