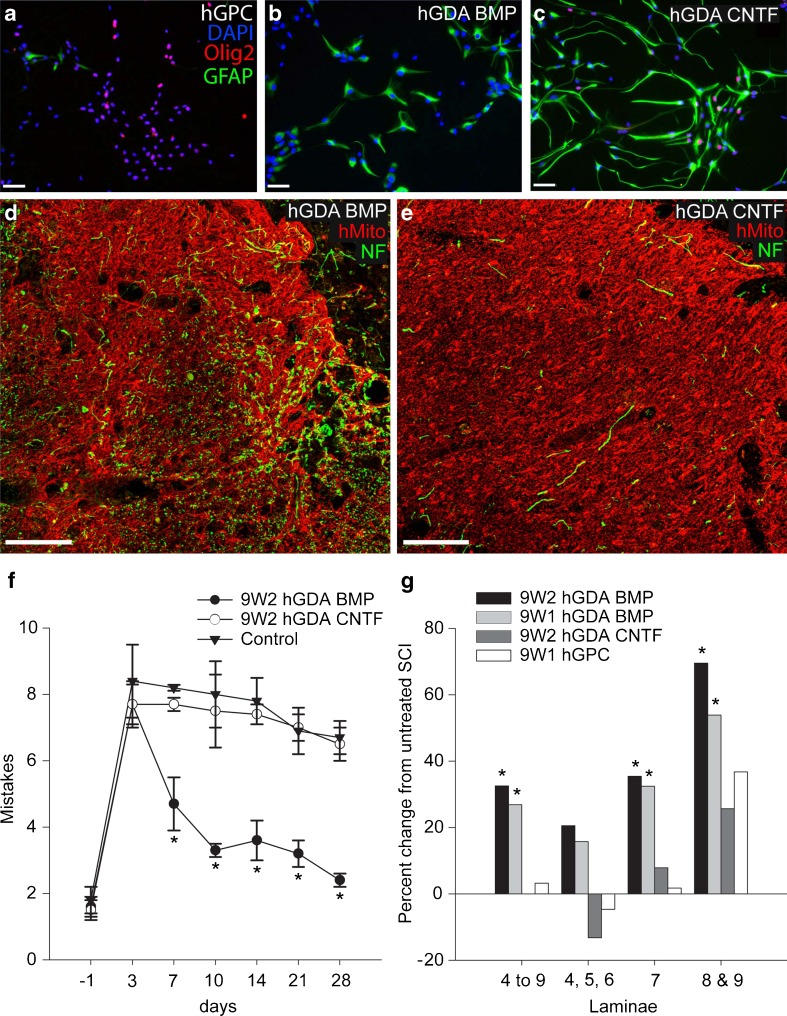
Fig. 5.
Astrocytes generated by exposing human glial precursor cells (hGPCs) to BMP (hGDAsBMP) are robust promoters of axonal regeneration and behavioral recovery, whereas astrocytes generated by exposing GRP cells to CNTF (hGDAsCNTF) and hGPCs themselves are not (a-c). Human GPCs grown in fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) (a) were induced to differentiate into astrocytes using BMP (b) or CNTF (c). Labeling with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (Alexa-488) demonstrates that both BMP and CNTF induce differentiation of human glial precursors into glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-expressing astrocytes, whereas Olig2 expression (Alexa-568) is not seen in hGDAsBMP. Scale bar = 50 μm. (d, e) Immunostaining for human mitochondrial marker (red channel) of histological cross sections at sites of injury revealed hGDAsBMP (d) and hGDAsCNTF (e) transplant masses spanning the dorsal-ventral and lateral-medial margins of injury sites. Co-labeling for neurofilament (NF) (green) and human mitochondrial marker (hMito) (red) shows a markedly higher density of axons within hGDAsBMP-treated injury sites (d) compared to hGDAsCNTF-treated injury sites (e). Survival = 5 weeks post injury/transplantation. Scale bar = 100 μm. (f) Human GDAsBMP promote robust locomotor recovery, but hGDAsCNTF and hGPCs do not. The graph shows the average number of mistakes per experimental group made during grid walk testing of locomotor recovery at 1 day before injury to 28 days after injury. In 2 separate experiments, hGDABMP transplanted animals (closed circles) performed significantly better than hGDACNTF or hGPC not shown) transplanted animals at all time points from 7 to 28 days postinjury/transplantation. The performance of hGDACNTF or hGPC (not shown) transplanted animals was not significantly different from control injured rats at all time points (2-way repeated measures analysis of variance; *p < 0.05). (g) Human GDABMP transplantation led to significant increases in numbers of neuronal nuclei-positive (NeuN+) neurons counted in a 1.8-mm length of spinal cord encompassing the injury site. Graphs show percentage changes in numbers of NeuN + neurons in laminae 4 to 9; laminae 4, 5, and 6; 7, 8 and 9 in spinal cords from animals that received transplants of 9 W2 or 9 W1 hGDAsBMP, hGDAsCNTF, or hGPCs and untreated control injuries