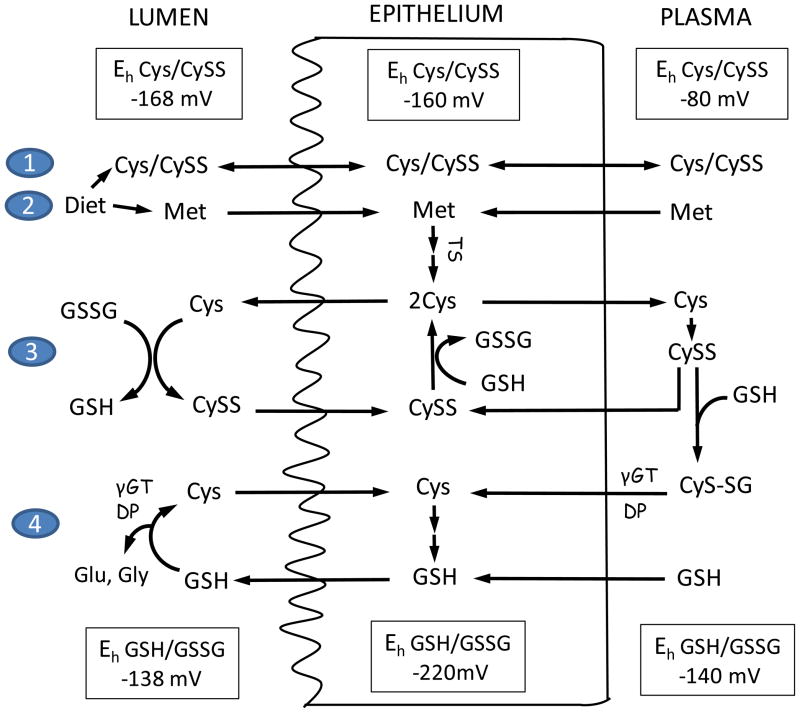
Figure 3. Homeostatic control of Cys/CySS redox status in intestinal lumen, intestinal epithelium, and plasma.
At the brush-border membrane, uptake of dietary Cys and methionine (1 & 2); Cys/CySS shuttle (3), and γ-glutamyl transferase (γGT) and dipeptidase (DP)-catalyzed hydrolysis of extracellular GSH (4) participate in Cys homeostasis. The Cys/CySS shuttle and luminal GSH hydrolysis maintains the Eh for luminal Cys/CySS at −168mV and that of GSH/GSSG at −138mV. Within the intestinal epithelium, CySS is reduced by GSH, the resultant Cys is exported or utilized in GSH synthesis. Additionally, intracellular Cys is increased through the trans-sulfuration (TS) of imported dietary or circulatory methionine (Met). Plasma Cys exists mainly as CySS, and the redox state of plasma Cys is controlled by thiol/disulfide exchange with liver-derived GSH. The hydrolysis of Cys-GSH mixed disulfide (CyS-SG) releases Cys which is taken into enterocytes by basolateral membrane associated transporters. The Eh for Cys/CySS and GSH/GSSG redox couples are tightly regulated at values of −80mV and −140mV, respectively. Luminal values of Eh for Cys/CySS and GSH/GSSG redox couples were taken from [69] and the plasma values were from [53,106].