Figure 1.
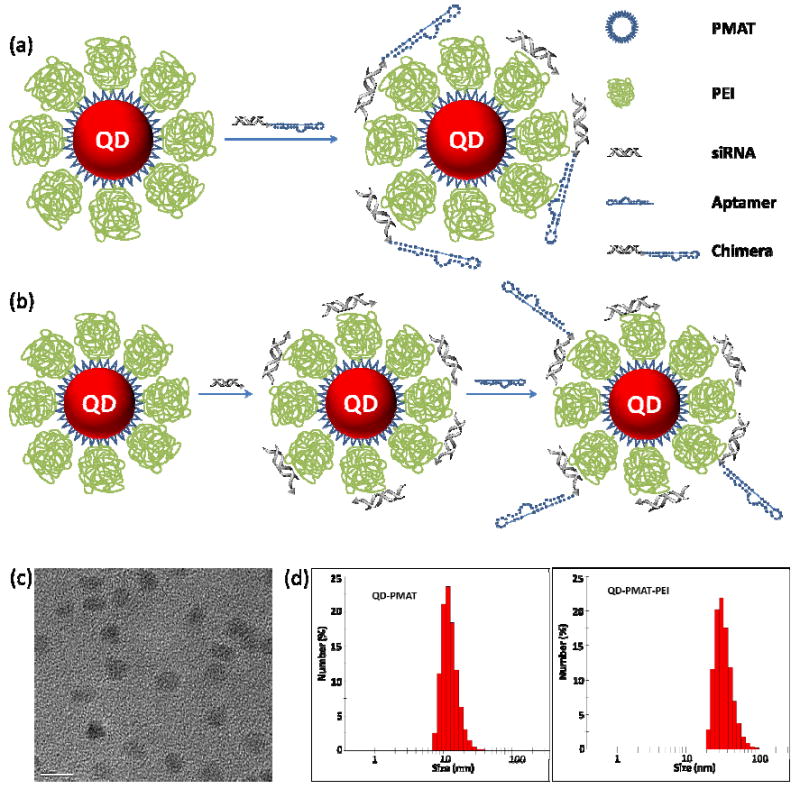
Schematic representation of cationic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of siRNA-aptamer chimera. (a) Immobilization of preformed siRNA-aptamer chimera onto positively charged QD-PMAT-PEI nanoparticles. The aptamer block collapsed on the carrier results in reduced binding activity. (b) Two-step immobilization of chimera on cationic nanoparticle surface. siRNA molecules with a thiol-reactive terminal group are first adsorbed on QD-PMAT-PEI surface to reduce the positive charge; subsequently aptamers with a single thiol group are brought in to form the siRNA-aptamer chimera on the nanoparticle surface. (c) TEM image of QD-PMAT-PEI nanoparticles (scale bar 10 nm). (d) Hydrodynamic diameter of QD-PMAT (12.1 ± 0.7 nm) and QD-PMAT-PEI (32.2 ± 4.5 nm) nanoparticles.
