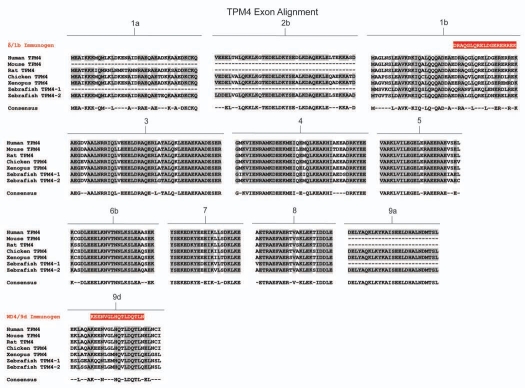
Figure 5.
Amino acid sequence comparison of the TPM4 gene from six animal species. Amino acid alignment of all exons contained within the TPM4 gene for selected members of chordata. Species included are human (Homo sapiens), mouse (Mus musculus) and rat (Rattus norviegicus) representing mammalians, chicken (Gallus gallus) representing birds, western clawed frog (Xenopus tropicalis) representing amphibians and zebrafish (Danio rerio) representing fish. Shaded areas and consensus sequence indicate regions of sequence conservation while unshaded regions represent areas of sequence divergence between the aligned species. Dashed lines within alignments imply that either the particular exon is not found within that species or that the exon in question has not been identified due to minimal genomic sequence information and lack of evidence from cDNA library sequences. Zebrafish contains two copies of the TPM4 gene, named TPM4-1 and TPM4-2 which are the result of a whole genome duplication event. Antibody immunogens for antibodies δ/1b and wd4/9d are presented as white text highlighted in red and are aligned with the region of the exon from which they were derived. The antibody immunogen for γ/9a (TPM3 gene) is also shown.