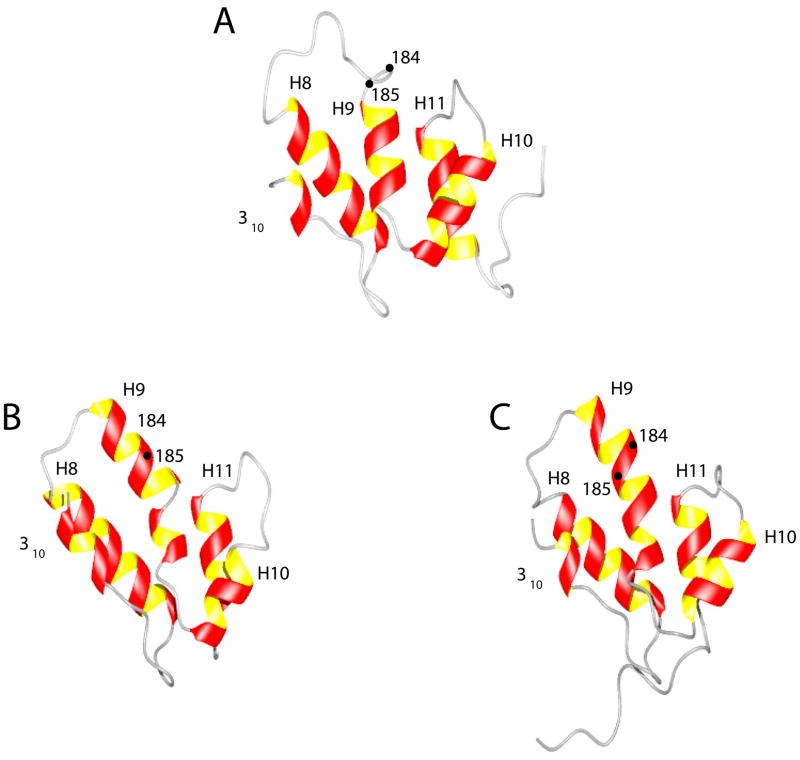
Figure 6.
Comparison of the CTD domains: (A) The CTD domain of the W184A/M185A-CA in this work. (B) The CTD domain from the wild-type antiparallel dimer CA crystal structure (24). (C) The CTD domain from the wild type CTD dimer NMR structure (8). The location of residues 184 and 185 is also shown. In the crystal structure and in the wt CTD-dimer NMR structure, helix-10 is longer and shows a bend. The hydrophobic groove formed by helices 9 and 10 has been a target for inhibitors such as CAI (14) and NYAD-13 (15). The CTD-CTD dimerization interface involving helix-10 has been targeted by inhibitors of dimerization (12,38). Further, helix-12 in the CTD domain has been suggested to be the binding site for human lysyl t-RNA synthetase (28) which is thought to play a critical role in targeting tRNALys for viral packaging.