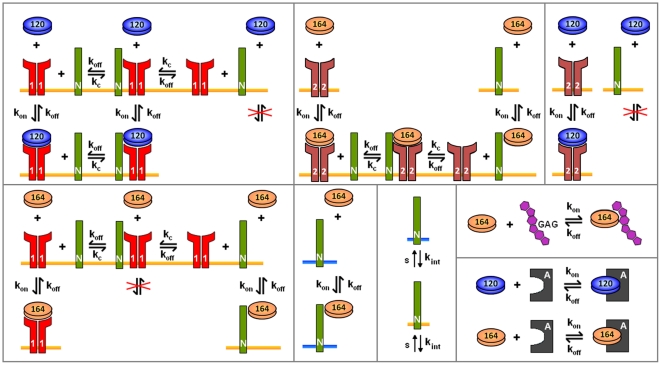
Figure 2. Molecular interactions.
The binding interactions of VEGF120 and VEGF164 are different. VEGF120 binds to VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 but not to NRP-1. VEGF164 binds to VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, NRP-1, and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains in the extracellular matrix. In simulations where the anti-VEGF agent (VEGF Trap) is added, both isoforms bind to the anti-VEGF agent to form a complex. Binding and unbinding of VEGF to receptors are denoted as kon and koff, respectively. kc denotes the coupling of NRP-1 and VEGFR-1 and of NRP-1 to VEGFR-2. While only the internalization of NRP-1 is shown, all VEGF receptors and complexes can be internalized at a rate kint. Similarly, while only the insertion of NRP-1 is shown, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 also appear via insertion at a rate s. The blue bar is used to distinguish NRP-1 expressed on the myocytes from NRP-1 on the endothelial cells (orange bars).