Fig. 7.
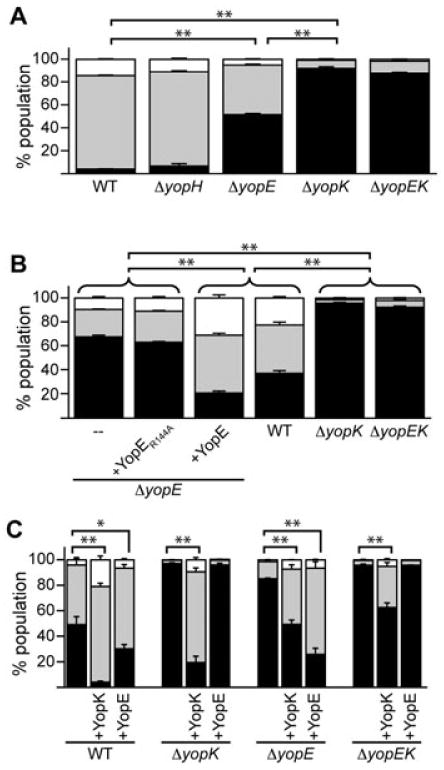
Regulation of translocation by YopK and YopE. A. CHO cells were infected with WT or mutant Y. pestis strains carrying the YopM-Bla reporter at moi = 10 for ∼3 h. Cells were stained with CCF2-AM and injection was quantified by flow cytometry. Infections were performed in triplicate and the entire experiment was repeated at least twice. The data shown are a representative data set from one experiment showing average injection levels and standard deviation error bars. High-level injection (blue cells) was compared using one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. B. ΔyopE Y. pestis strains were complemented with plasmids expressing either YopE or a GAP-deficient YopE (YopER144A), used to infect CHO cells, and injection of the YopM-Bla reporter was measured. Assays and analysis were performed as in (A). C. Y. pestis strains were transformed with plasmids expressing YopK or YopE in addition to the YopM-Bla reporter and used to infect CHO cells as in (A). Student's t-test was performed to demonstrate significant differences in high-level injection relative to empty parent strains. For all panels, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001.
