Figure 3.
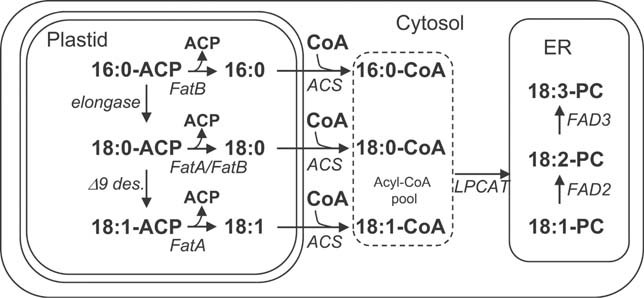
Generalised scheme of the biosynthesis of the five common fatty acids and the main enzyme steps involved. The first three fatty acids (16:0, 18:0 and 18: 1Δ9) are produced by de novo synthesis and desaturation in the plastids. Elongation and desaturation are carried out while the fatty acids are attached to acyl carrier protein (ACP). After removal of the ACP group by acyl-ACP thioesterases (FatA or FatB), the fatty acids are exported from the plastid and incorporated into the cytosolic acyl-CoA by the action of an acyl-CoA synthetase (ACS). 18:1Δ9 is then acylated onto PC, mainly by the action of the LPCAT. Further desaturations of the 18:1Δ9 to 18:2Δ9,12 and 18:3Δ9,12,15 are catalysed by FAD2 and FAD3 while the acyl substrates are acylated to PC. The further synthesis of glycerol lipids from acyl-CoA are depicted in Fig. 4
