Fig. 1.
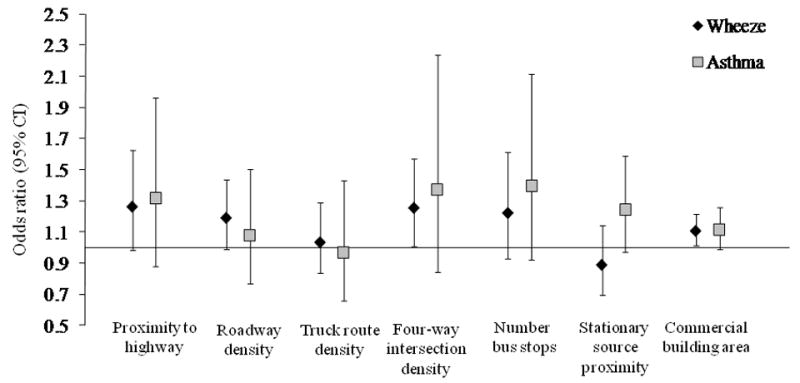
Associations of GIS variables measured repeatedly between birth and age 5 years with concurrent wheeze and parental report of physician-diagnosed asthma. Data points and error bars describes the odds ratio and 95% CI, respectively, for the association of an interquartile range increase in the magnitude of the GIS variable with the presence of wheeze or diagnosis of asthma by a physician in previous 12 months, adjusted for sex, ethnicity, presence of smoker in the home, annual income, residential cockroach allergen concentration, residential mouse allergen concentration, age, and age by GIS variable interaction.
