Figure 3. Synergistic effect of cellular microRNAs on regulating inflammation during HPAI infection.

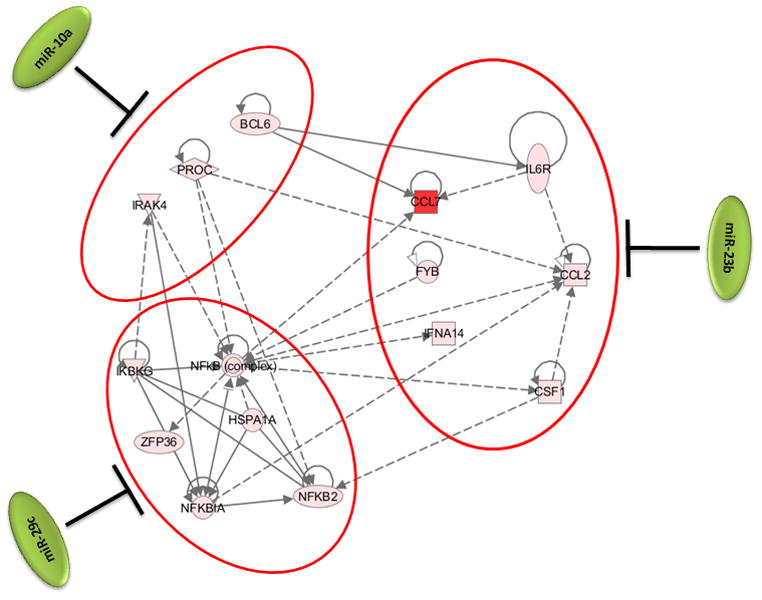
3a: Expression patterns of cellular microRNAs miR-10a, miR-29C and miR-23b and their inversely correlated target genes associated with the inflammation in HPAI infected lungs. Red color represents microRNA or target gene with increased expression in HPAI- or 2:6-infected samples, relative to Tx-infected samples. Green represents microRNA or target gene with decreased expression in HPAI- or 2:6- infected samples, relative to Tx-infected samples. 3b: Network demonstration of the functional connection between inversely correlated target genes associated with inflammation during the HPAI infection. Red color indicates increased expression in comparison with the Tx infected samples. Both figures represent the results from Day 7 post infection. HPAI: Highly pathogenic virus; 2:6: medium pathogenic virus.
