Fig. 1.
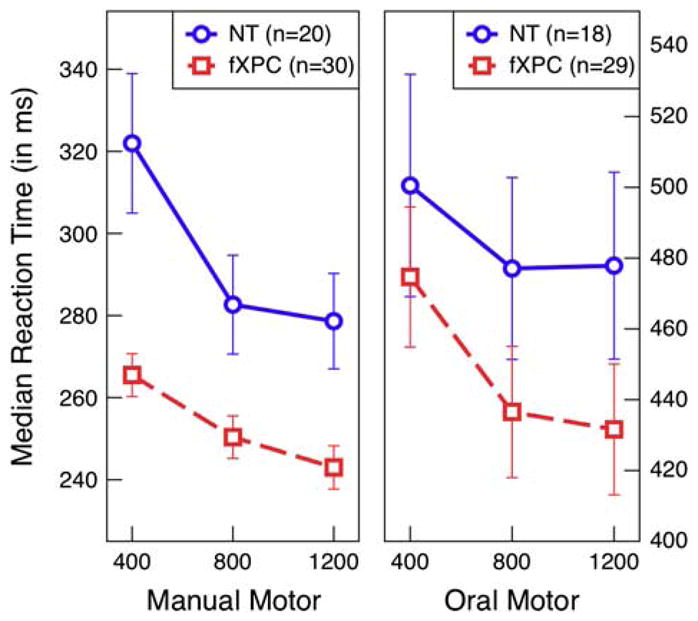
Oral motor reaction times ranged from 248 to 782 ms (M =461.24, SEM =7.92) and were overall slower than manual motor reaction times, which ranged from 203 to 515 ms (M =268.14, SEM =3.42). Group analyses of manual motor and oral reaction time show that female fXPCs, as a group, responded faster than female NT controls, p =.003 and p =.01, respectively. For both task versions, reaction times decreased as the delay between trials were longer, p <.0001, but did not differ between the groups, p >.28. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
