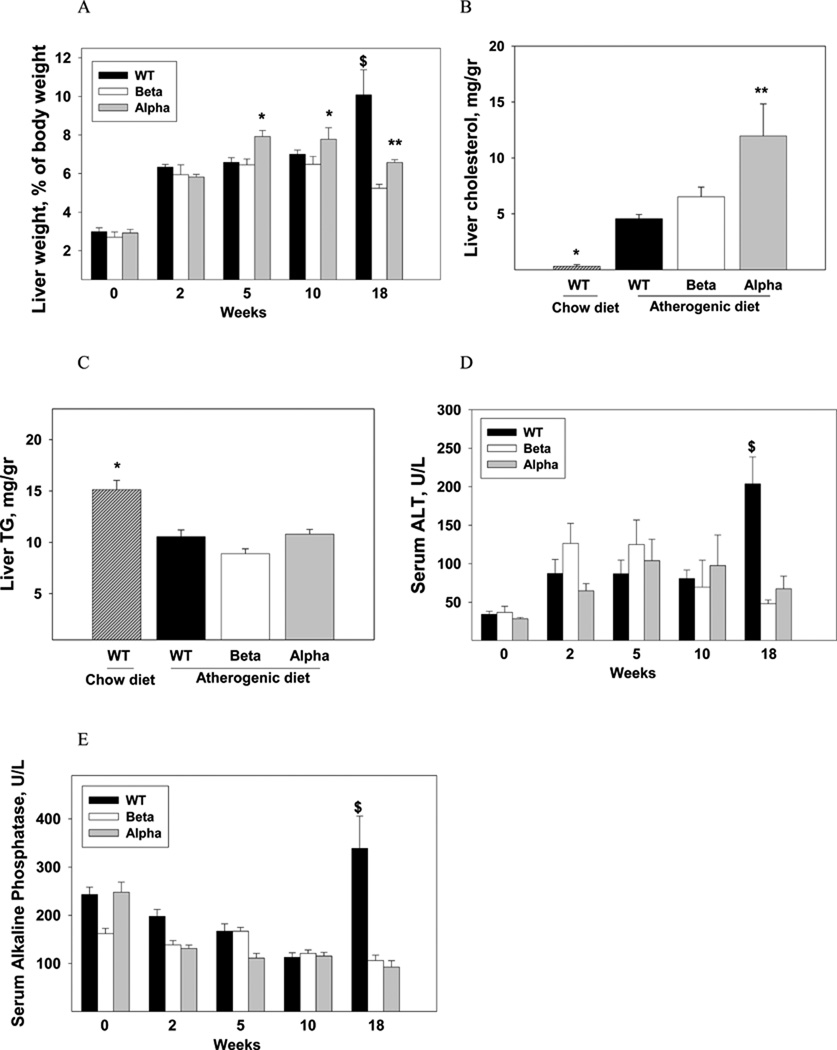
Figure 2. The effect of IL-1α or IL-1β deficiency on atherogenic diet-induced steatosis and steatohepatitis.
Liver to body weight ratio (A) in WT, IL-1β KO (Beta) and IL-1α KO (Alpha) mice (n=5 in each group) were determined at baseline and after 2, 5, 10, and 18 weeks of the atherogenic diet. Data represent mean±SE of each group. *p<0.05 compared to WT and IL-1β KO mice, **p<0.05 compared to IL-1β KO mice, $p<0.05 compared to IL-1β KO and IL-1α KO mice. Hepatic cholesterol (B) and TG (C) levels were determined in chow-fed WT and WT, IL-1β KO (Beta) and IL-1α KO (Alpha) mice (n=5 in each group) after 10 weeks of the atherogenic diet. Data represent mean±SE of each group. *p<0.05 compared to atherogenic diet-fed WT, IL-1β KO (Beta) and IL-1α KO (Alpha) mice. **p<0.05 compared to atherogenic diet-fed WT and IL-1β KO mice. Serum levels of ALT (D) and alkaline phosphatase (E) were determined in mice described in (A). Data represent mean±SE of each group, $p<0.05 compared to IL-1β and IL-1α KO mice.