Fig. 5.
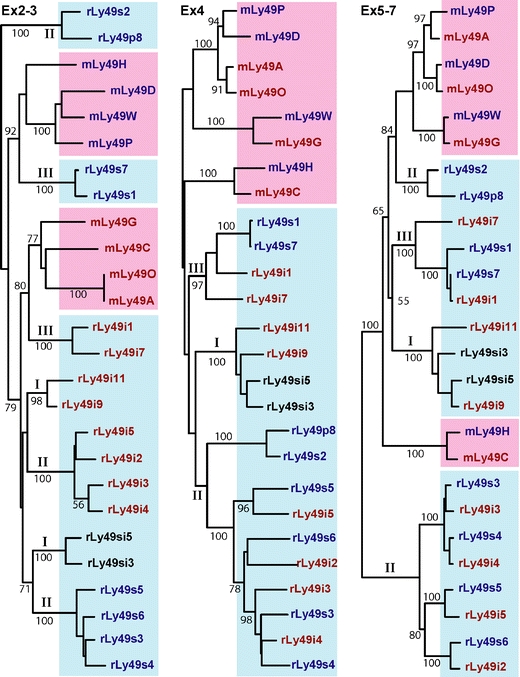
Exonwise comparisons between selected rat and mouse KLRA (Ly49) receptors. Mouse sequences m and red background; rat sequences—r and blue background. The comparisons were made at the amino acid level, with sequences grouped into STPs (cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains encoded by exons 2 and 3), the stalk (encoded by exon 4), and the lectin-like domain (encoded by exons 5–7). Red—ITIM-bearing receptors, blue—non-ITIM-bearing and transmembrane arginine, black—receptors with both features (“bifunctional”). Branches with roman numbers I–III indicate rat receptors encoded by chromosomal segments (blocks) I–III (see text). Arabic numbers indicate bootstrapping values in percent (1,000 iterations). It should be noted that the STP of the activating variants form three separate branches and persistently do so with variation of parameters when tested both at the amino acid and at the nucleotide level and when the exons encoding the cytoplasmic tail and the TM are analyzed separately or together
